

Blockchain Basics: What It Is and Why It Matters
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions securely and transparently across a network of computers. Although best known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, blockchain has many other impactful applications in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and logistics.
What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a shared database maintained by a distributed network of nodes. It consists of "blocks" of data that are linked using cryptographic hashes. Once data is recorded on a block and added to the chain, it becomes immutable and visible to the entire network.
Each block typically includes:
A list of validated transactions
A timestamp
A reference to the previous block (hash)
This design makes blockchain secure, transparent, and nearly tamper-proof.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain works through the consensus of multiple computers, often referred to as nodes. Here's how it works in simple terms:
A transaction is requested.
A block representing the transaction is created.
The block is sent to all nodes in the network.
Nodes validate the block via consensus mechanisms (e.g. Proof of Work).
The verified block is added to the chain permanently.
This structure allows blockchain to function without a central authority.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization: No single point of control or failure.
Transparency: All transactions are publicly verifiable.
Immutability: Once added, data cannot be changed.
Security: Uses cryptography to link and protect blocks.
Types of Blockchains
There are several types of blockchains, each serving different needs:
Public Blockchains (e.g. Bitcoin): Open to anyone, decentralized.
Private Blockchains: Access restricted to selected participants.
Consortium Blockchains: Shared control by multiple organizations.
Hybrid Blockchains: Mix of public and private characteristics.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Although blockchain is most famously associated with different types of cryptocurrencies, and crypto trading, but its applications are vast and diverse:
Cryptocurrency: Secure and transparent value transfers.
Banking: Faster settlements and reduced fraud.
Healthcare: Tamper-proof medical records.
Supply Chains: End-to-end product tracking.
Voting Systems: Immutable digital ballots.
Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements coded on the blockchain.
Challenges of Blockchain
While blockchain holds enormous potential, it’s not without its challenges:
Scalability: Slow transaction speeds on some networks.
Energy Use: High power consumption for mining.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Varies by region and industry.
Complexity: Barriers to adoption due to technical learning curve.
The Future of Blockchain
Advancements like Layer 2 solutions, proof of stake, and blockchain interoperability are addressing current limitations. Governments and enterprises are exploring new use cases in digital identity, fraud prevention, and decentralized finance.
Conclusion
With its promise of transparency, security, and decentralization, blockchain technology has potential applications across countless industries. While it still faces hurdles, the continued innovation and exploration into blockchain’s uses suggests that it could revolutionize how data and transactions are handled.
Whether it’s a tool for transforming financial systems, securing healthcare data, or building decentralized networks, blockchain is here to stay. It may play a vital role in the future of digital infrastructure.
Trade Smarter Today
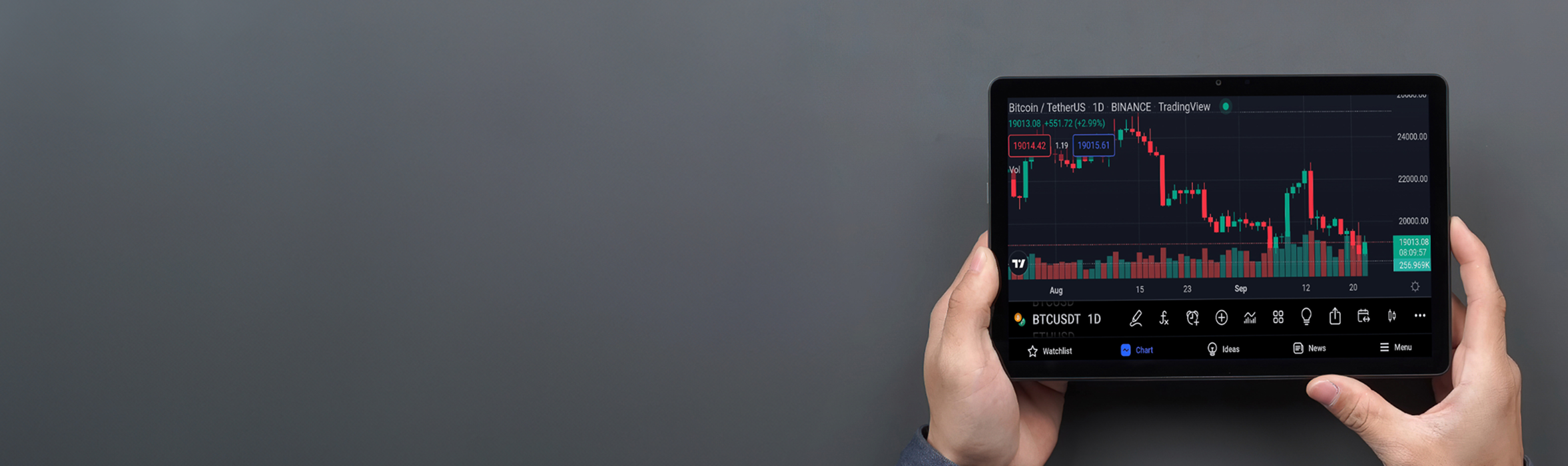





Account
Account
Instantly







