인기 기사
- USD/CAD flattens around 1.3885 ahead of the US PPI and Retail Sales data.
- The Fed is unlikely to cut interest rates in the policy meeting later this month.
- Investors seek fresh cues for BoC’s monetary policy outlook.
The USD/CAD pair trades flat around 1.3885 during the European trading session on Wednesday. The Loonie pair consolidates ahead of the United States (US) Producer Price Index (PPI) data for October and November, and the Retail Sales data for November.
However, the impact of the data is expected to be limited as they are not the latest, and it seems unlikely to influence market expectations for the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook.
According to the CME FedWatch tool, the Fed is certain to hold interest rates steady in the current range of 3.50%-3.75% in the policy meeting later this month.
Meanwhile, the Canadian Dollar (CAD) trades steadily, with investors looking for fresh cues on the Bank of Canada’s (BoC) monetary policy outlook. This week, investors will focus on the monthly Manufacturing and Wholesale Sales data for November, which will be released on Thursday.
USD/CAD technical analysis
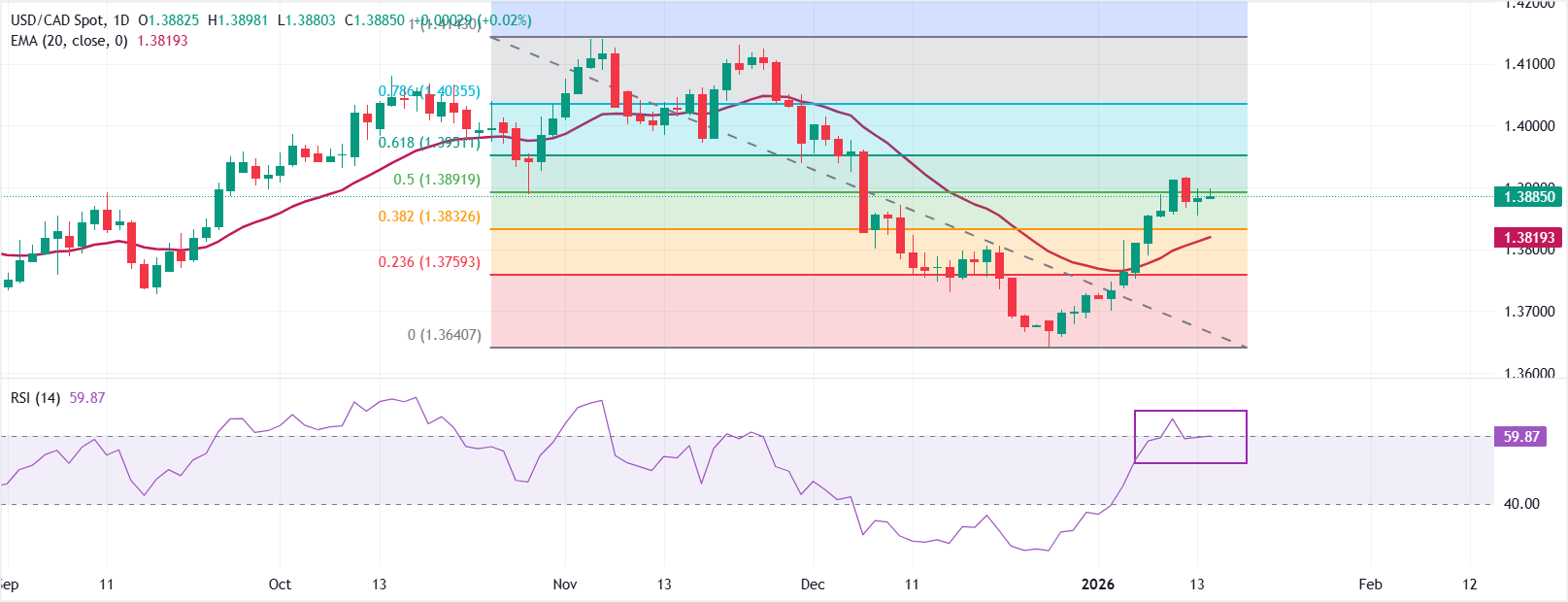
USD/CAD trades steadily near 1.3885 as of writing. Price holds above the rising 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 1.3819, keeping the short-term bias positive.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) at 59.87 signals improving bullish momentum without overbought conditions.
Measured from the 1.4143 high to the 1.3641 low, the 50% Fibonacci retracement at 1.3892 acts as initial resistance, and a close above it could open a test higher toward 61.8% Fibo retracement at 1.3931. Failure to clear this barrier would keep consolidation intact, while a break above would underpin an extension.
(The technical analysis of this story was written with the help of an AI tool.)
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.








