Key Takeaways
Margin in forex is collateral, not a fee. It is the deposit required to open and maintain leveraged trades; for example, 100 to 1 leverage means US$1,000 margin controls a US$100,000 position.
Margin level in forex is calculated as (equity ÷ used margin) × 100 percent. As margin level falls toward about 100 percent, brokers may restrict new trades or trigger margin call and stop out rules.
Free margin in forex equals equity minus used margin and shows your capacity for new trades and drawdowns. Used margin is tied up in open positions, so monitoring both is critical.
Margin calls are risk controls in forex margin trading. When equity drops too low, brokers may warn, restrict new orders or automatically close positions based on their margin level thresholds.
Understanding how margin works in forex, including margin, free margin, margin level and margin calls. Supports better position sizing, conservative leverage and long term risk management.
What is Margin in Forex?
Margin in forex trading is the amount of capital a trader must deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is not a fee but collateral set aside to cover potential losses. Margin is usually expressed as a percentage of the total trade size. For example, with 100 to 1 leverage, opening a US$100,000 position requires a US$1,000 margin deposit. This simple example shows how forex margin lets you control larger trades but also increases risk if the market moves against you.
Margin Level in Forex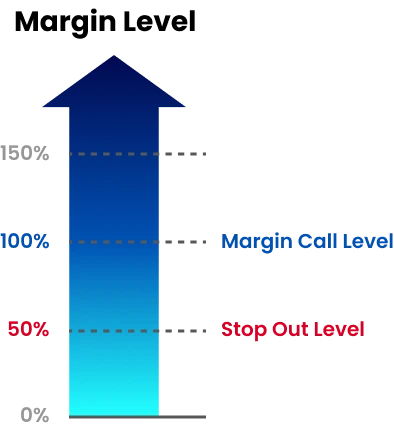
What is Margin Level in Forex?
In forex trading, the margin level is the percentage that represents the ratio between a trader’s equity and used margin. It shows how much capital is currently available relative to the margin requirements.
How to Calculate Margin Level in Forex
Margin level in forex is calculated as (equity ÷ used margin) × 100
For example, if a trader has US$1,000 equity and US$500 in used margin, their margin level is 200 percent. This is the standard way traders describe how to calculate margin level in forex.
Rearranging the same relationship also shows how to calculate margin in forex:
Used margin equals equity ÷ by (margin level ÷ 100)
Importance of Margin Level in Forex
Brokers in forex margin trading closely monitor margin level in forex accounts to control risk. When it falls below a set threshold, typically around 100 percent, the broker may alert the trader or restrict new trades.
What is Margin Call in Forex?
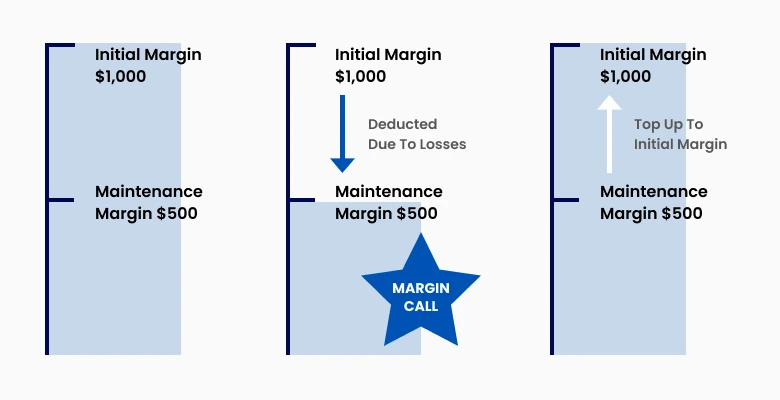
A margin call in forex is a warning that your equity has fallen below the broker’s required margin level. It usually happens when open losses consume your free margin and shows very clearly how margin works in forex when markets move against you.
It serves as a risk management tool to protect both the trader and the broker in forex margin trading. Margin calls prevent further losses by requiring the trader to add funds or close positions.
Purpose of a Margin Call
It serves as a risk management tool to protect both the trader and the broker in forex margin trading. Margin calls prevent further losses by requiring the trader to add funds or close positions.
How to Avoid Margin Calls
Managing risk through appropriate position sizes and stop-loss orders can reduce the likelihood of a margin call, as can choosing leverage levels that align with one's risk tolerance.
Free Margin vs. Used Margin

What is Free Margin in Forex?
Free margin in forex is the amount of money in your trading account available for new trades. It is calculated as equity minus used margin and shows how much room you have before a margin call.
What is Used Margin?
Used margin in forex is the amount of money locked in open positions to support your current leveraged exposure. Once those trades are closed, the used margin is released and becomes free margin again.
Importance of Margin in Forex
Knowing the difference between free margin and used margin is essential for managing positions effectively, especially when multiple trades are open simultaneously.
Why Forex Margin Matters

Understanding what margin is in forex and how margin level, free margin and margin calls interact is essential for long term risk management.
Risk Management: Forex margin is essential for managing trading risk. By controlling leverage and margin levels, traders can prevent overexposure and avoid excessive losses.
Maintaining a Sustainable Balance: Balancing leverage with free margin ensures traders have enough capital to withstand market fluctuations and avoid forced liquidations.
Empowering Strategy: A proper understanding of forex margin allows traders to develop better strategies, helping them to maximize gains while minimizing risks.
Common Mistakes in Managing Forex Margin
Over-leveraging: Using high leverage without understanding margin requirements can lead to rapid losses, especially in volatile market conditions.
Ignoring Margin Calls: Failing to respond to margin calls or disregarding margin levels increases the risk of forced liquidation.
Not Monitoring Free Margin: Monitoring free margin is critical, as it determines a trader’s ability to open additional trades and manage existing ones.
Mastering Forex Margin for Better Trading

In short, understanding forex margin is a foundational aspect of successful forex trading. From the initial deposit needed to open a trade to managing margin calls, mastering these principles enables traders to leverage opportunities and manage risk effectively.
Whether you are new to forex or looking to deepen your skills, knowing how forex margin functions can give you an edge in the market.
To explore advanced tips and strategies in forex trading, TMGM offers extensive educational resources and tools to help traders understand Forex margin and leverage it to their advantage. Visit TMGM and enhance your trading expertise today.