What Is Bitcoin (BTC)? How It Works, How to Buy and Mine It
Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency (a virtual currency) designed to act as money and a form of payment outside the control of any person, group, or entity. This removes the need for trusted third-party involvement (e.g., a mint or bank) in financial transactions. Bitcoin was introduced to the public in 2008 by an anonymous creator known as Satoshi Nakamoto and has since evolved into the world’s most recognized cryptocurrency. Beyond its role as a digital currency, Bitcoin has become a highly traded asset across global markets. Its price volatility attracts active traders who use various strategies like day trading and swing trading to capitalise on short-term movements. Traders often apply popular technical indicators such as RSI, MACD, or fibonacci retracement to identify entry and exit points. As the market matures, Bitcoin continues to be at the center of crypto trading activity—offering opportunities for both speculative trades and long-term trading strategies using advanced CFD Trading platforms.
Key Takeaways
Bitcoin is the end product of the work of many people, but it is generally accepted that Satoshi Nakamoto created it and introduced it in 2008.
Bitcoin is the public blockchain used to create and manage the cryptocurrency of the same name.
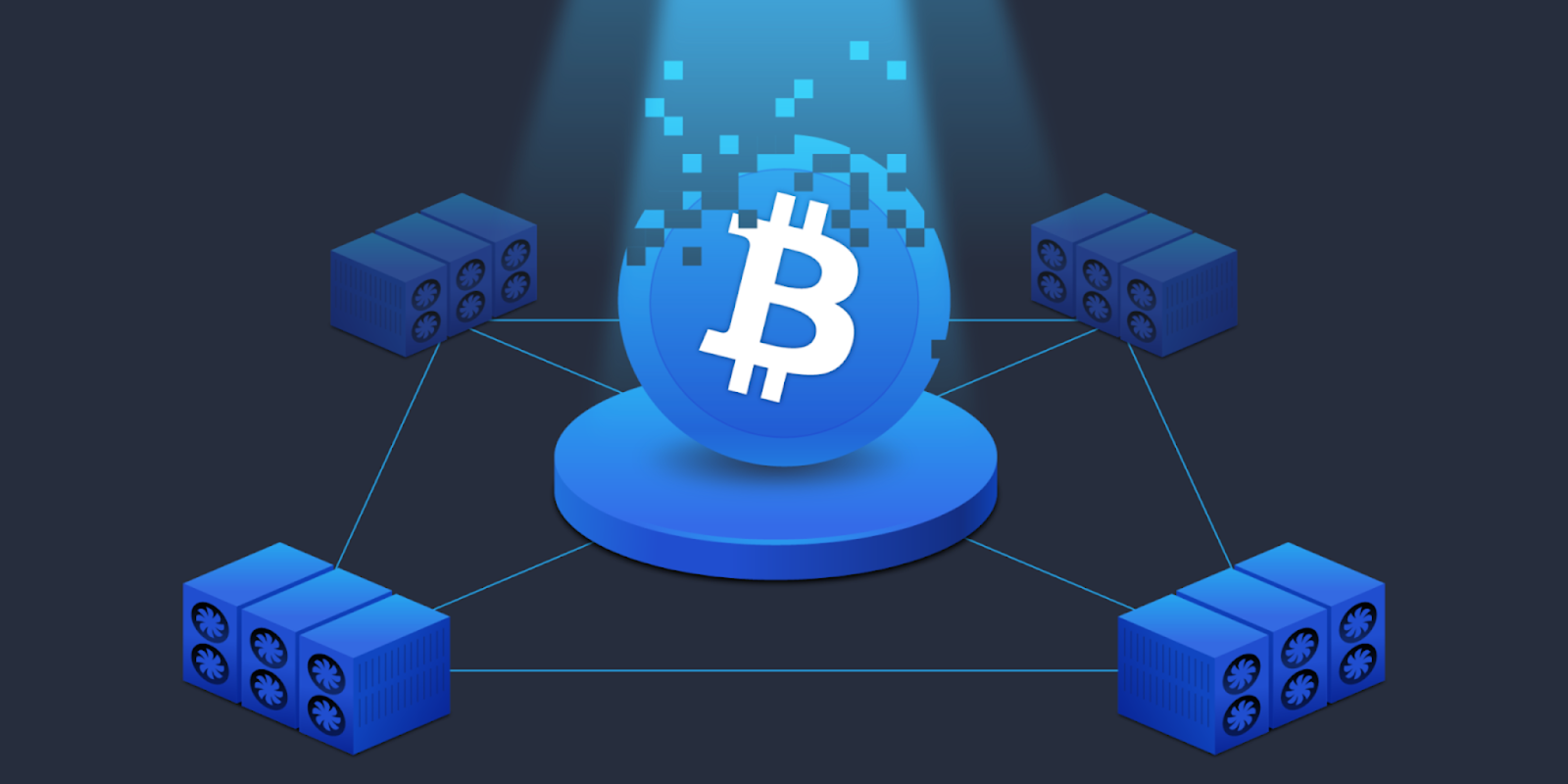
Bitcoin mining is the race between miners to hash block information, find the solution to a hashing problem, and add a block to the blockchain. The winning miner is rewarded with bitcoins.
Bitcoin can be used by speculators, investors, and consumers for purchases or value exchange.
There are many risks involved with investing in and using bitcoins, including volatility, fraud, and theft.
What Is Bitcoin (BTC) and How Does It Work?
Figure 1: Bitcoin mining and the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network
What Is a Bitcoin (BTC)?
The domain name Bitcoin.org was registered in August 2008. It was created by Satoshi Nakamoto and Martti Malmi, who worked with the anonymous Nakamoto to develop Bitcoin.
How and When did Bitcoin (BTC) Start?
In October 2008, Nakamoto announced to the cryptography mailing list at metzdowd.com: "I've been working on a new electronic cash system that's fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party." The now-famous white paper published on Bitcoin.org, entitled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," would become the Magna Carta for how Bitcoin operates today.
Bitcoin Genesis Block
The first Bitcoin block was mined on Jan. 3, 2009. Block 0, also known as the genesis block, contains the text "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on the brink of second bailout for banks," perhaps proof that the block was mined on or after that date.
Bitcoin Mining Rewards Over Time
Bitcoin rewards are halved every 210,000 blocks. For example, the block reward was 50 new bitcoins in 2009. On May 11, 2020, the third halving occurred, bringing the reward for each block down to 6.25 bitcoins. The fourth halving occurred in April 2024 and lowered the reward to 3.125 bitcoins. The next halving should happen in mid-2028 and reduce the reward to 1.5625 BTC.
Bitcoin Units and Denominations
One Bitcoin (BTC) is divisible to eight decimal places (100 millionths of one bitcoin), and this smallest unit is referred to as a satoshi.
The Cryptography Mailing List announced the first version of the Bitcoin software on Jan. 8, 2009. On Jan. 9, 2009, Block 1 was mined, and Bitcoin mining began.
Bitcoin (BTC) and Blockchain Technology Explained
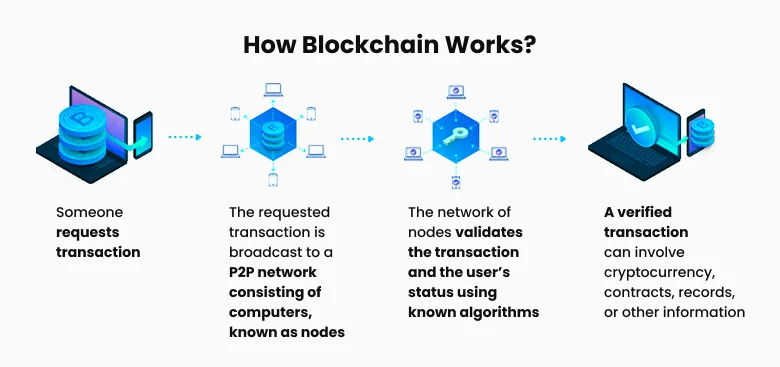
Figure 2: How blockchain works
Bitcoin as a form of digital currency isn't hard to understand. For example, if you own a Bitcoin, you can use your cryptocurrency wallet to send smaller portions of that Bitcoin as payment for goods or services. By contrast, the way Bitcoin works is very complex.
Bitcoin (BTC) Blockchain Explained
A blockchain is a distributed ledger, a shared information database chained together via cryptographic techniques. "Distributed" means that it is stored on many computers rather than a centralized server location, as most data storage typically does.
A network of automated programs installed on these computers maintains the blockchain and performs the functions necessary for it to operate.
A block on a blockchain is a file that contains a block header, transaction counter, and the transactions recorded in the block. The transaction counter lists the transactions in the block, while the block header is made up of several elements:
Software version: Which version the blockchain is running (sometimes called the magic number)
Previous block hash: The encrypted information of the prior block
Merkle root: A single hash (encrypted information) that contains all the hashed information of earlier transactions
Timestamp: The date and time the block was opened
Difficulty target: The current network difficulty problem miners are attempting to solve for
Nonce: Short for "number used once," which is used to solve the mining problem and open the block.
As noted, each block contains the hashed information of the previous block. This creates a chain of encrypted blocks (files) that contain information from all previous blocks, going back to the first block of the blockchain.
Bitcoin (BTC) Encryption and Security
Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm to encrypt (hash) the data stored in the blocks on the blockchain. Simply put, transaction data stored in a block is encrypted into a 256-bit (64-digit) hexadecimal number. That number contains all the transaction data and information linked to the blocks before that block.
While the data in a block is encrypted and used in the next block, the block is not inaccessible or non-readable. The hash is used in the next block, then its hash is used in the next, and so on, but all blocks can be read. This ensures that blocks cannot be changed without changing all other blocks and ensures anyone can audit the blockchain.
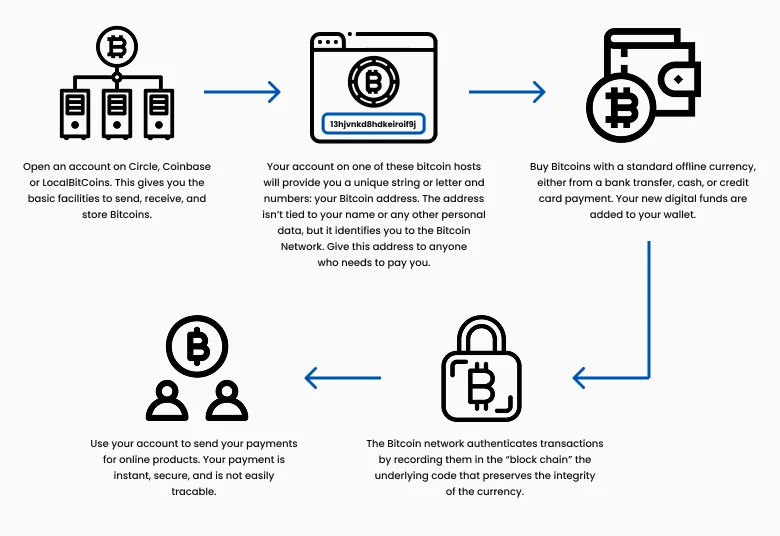
How To Buy Bitcoin (BTC)
If you don't want to mine Bitcoin, you can buy it using a cryptocurrency exchange. Most people cannot purchase an entire BTC because of its price, but you can buy portions of one BTC on these exchanges in fiat currency, such as U.S. dollars.
For example, you can buy a bitcoin on Coinbase or Binance by creating and funding an account using your bank account, credit card, or debit card.
Then, you can head to spot crypto, spot bitcoin or your spot wallet, in order to actually buy and own bitcoin using your crypto exchange (CEX) wallet. It is usually safe (for reputable exchanges like Coinbase and Binance) and liquid because you can safely store them there and sell it quickly when you need to.
Step-by-Step Guide to Bitcoin (BTC) Mining
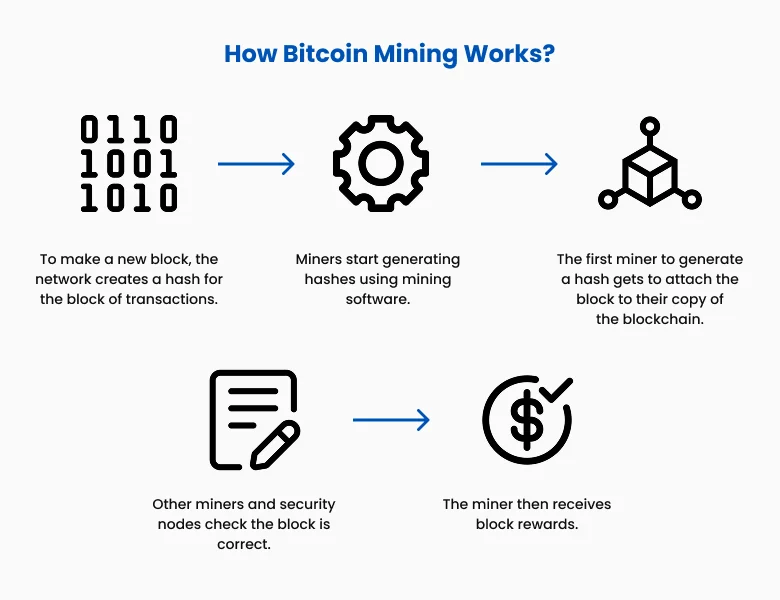 Figure 3: How Bitcoin Mining works
Figure 3: How Bitcoin Mining works
A variety of hardware and software can be used to mine Bitcoin. When the Bitcoin blockchain was first released, it could be mined competitively on a personal computer. However, as it became more popular, more miners joined the network, which lowered the chances of being the one to solve the hash.
You can still use your personal computer as a miner if it has newer hardware, but the chances of solving a hash individually utilizing a home computer are minuscule.
This is because you're competing with a network of miners that generate around 745 quintillion hashes (as of Dec. 5, 2024) per second. Machines—called Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) built specifically for mining—can generate more than 400 trillion hashes per second. In contrast, a computer with the latest hardware hashes around 100 megahashes per second (100 million).
Bitcoin Mining Methods and Strategies
There are two hardware options available for Bitcoin mining and several software options.
You can use your existing computer and mining software compatible with Bitcoin software and join a mining pool. Mining pools are groups of miners that combine their computational power to compete with large ASIC mining farms. There are many mining programs and pools you can join. Two of the most well-known programs are CGMiner and BFGMiner. Foundry Digital, Antpool, F2Pool, ViaBTC, and Binance.com are the most popular pools.
If you have the financial means, you could purchase an ASIC miner. You can generally find a new one for around $10,000, but miners sell used ones as they upgrade their systems. Consider some significant costs, such as electricity and cooling, if you purchase one or more ASICs. Remember that using one or two ASICs is still no guarantee of rewards as you compete with businesses with large mining farms of tens, if not hundreds, of thousands of ASICs. For example, Bitcoin mining firm CleanSpark claims to have 195,059 miners deployed.
Joining a pool can increase your chances of being rewarded bitcoins, but rewards are significantly decreased because they are shared. When choosing a pool, it's important to find out how it pays out rewards and fees and read some mining pool reviews.
How to Use Bitcoin for Payments
Figure 4: How to use Bitcoins
Bitcoin was initially designed and released as a peer-to-peer payment method. However, its use cases are growing due to its increasing value, competition from other blockchains and cryptocurrencies, and developments on blockchains that process information for the Bitcoin blockchain.
How to Pay With Bitcoin
Bitcoin is accepted as a means of payment for goods and services at many merchants, retailers, and stores.
Brick-and-mortar stores that accept cryptocurrencies will generally display a sign that says "Bitcoin Accepted Here." Transactions can be handled with the requisite hardware terminal or wallet address through QR codes and touchscreen apps. An online business can easily accept Bitcoin by adding this payment option to its other online payment options: credit cards, PayPal, etc.
To use your Bitcoin, you need a cryptocurrency wallet. Wallets are your blockchain interface and can hold the private keys to your bitcoins. You must enter these keys when you conduct a transaction.
How to Invest in Bitcoin or Trade Bitcoin
Investing in Bitcoin can take various forms, but two of the most common are buying the asset directly or trading it via Contracts for Difference (CFDs). Buying Bitcoin directly involves using a cryptocurrency exchange to purchase and store the coins in a digital wallet, often for long-term holding. This method exposes you to full price volatility, wallet security risks, and custodial fees.
On the other hand, trading Bitcoin CFDs or Crypto CFDs allows you to speculate on the price movement of Bitcoin without owning the actual asset. Crypto CFD trading is particularly suitable for short-term traders who want to profit from both rising and falling Bitcoin prices. With TMGM’s trading platform, you can access Bitcoin CFDs or Crypto CFDs with competitive spreads, fast execution, and the flexibility to apply leverage according to your risk appetite.
Additionally, Crypto CFDs trading removes the need for crypto wallets and gives you access to advanced charting tools and real-time price feeds. Whether you’re reacting to macroeconomic events, central bank policies, or crypto news, Crypto CFD trading offers more control and strategic versatility compared to traditional investing.
Summary: Should I Invest in Bitcoin?
Bitcoin had a price of $7,167.52 on Dec. 31, 2019, and a year later, it had appreciated more than 300% to $28,984.98. It continued to surge in the first half of 2021, trading at a record high of $69,000 in November 2021. It then fell over the next few months to hover around $40,000 and rose with increasing speed in 2024 to more than $100,000.
Due to such price movements, many people purchase Bitcoin for its investment value rather than its ability to act as a medium of exchange. However, its lack of guaranteed value and digital nature mean its purchase and use carry several inherent risks.
Many investor alerts issued by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) concern Bitcoin investing. Besides looking at the Bitcoin Outlook for 2025, there are a few risks that we need to be aware of.
Here are some of the risks that you're exposed to when trading or investing in Bitcoin:
Regulatory risk: The continuous battle between cryptocurrency-related projects and regulators makes longevity and liquidity an unknown. As of December 2024, the authorities do not consider Bitcoin a security, but that stance could change.
Security risk: Most individuals using Bitcoin have not acquired their tokens through mining operations. Instead, they buy and sell Bitcoin and other digital currencies on popular cryptocurrency exchanges. These exchanges are entirely digital and are at risk from hackers, malware, and operational glitches.
Insurance risk: Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are not insured by the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC) or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). However, some exchanges provide insurance through third parties. For instance, Gemini and Coinbase offer cryptocurrency insurance, but only for system failures or cybersecurity breaches. Any cash deposits you've made at either exchange might be eligible for "pass-through" FDIC coverage.
Fraud risk: Even with the security measures inherent within a blockchain, there are still opportunities for fraudulent activity.
Market risk: As with any investment, Bitcoin values can fluctuate. Indeed, the currency's value has seen wild price swings over its short existence. Subject to high-volume buying and selling on exchanges, it is highly sensitive to related news events.
Bitcoin Regulation and Legal Considerations
Figure 5: Bitcoin Legality Around the World
As with any new technology, it has been challenging to regulate Bitcoin. The U.S. administration seeks to impose regulations on cryptocurrency but walks a tightrope in trying not to throttle a growing and economically beneficial industry.
U.S. enforcement agencies continue to rely on existing securities, commodities, and tax laws. Still, as of December 2024, no legislative attempts have gained much attention from the country's law-making bodies.
The European Commission's long-anticipated Markets in Crypto Assets legislation came into force in 2023, setting the stage for cryptocurrency regulations in the European Union.
India banned several exchanges in December 2023 and continues to delay reviewing any legislation regarding Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Summary: Should I Invest in Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency introduced to the public and intended to be used as a form of payment outside legal tender. Since its introduction in 2009, Bitcoin's popularity has surged, and its blockchain uses have expanded.
Though the process of generating Bitcoin is complex, investing in it is more straightforward. Investors and speculators can buy and sell Bitcoin on crypto exchanges. As with any investment, particularly one as new and volatile as Bitcoin, investors should consider whether Bitcoin is the right investment.
Start Your Bitcoin Journey Today
Bitcoin’s price movements present exciting opportunities for traders, and TMGM provides a secure and professional platform to help you capitalize on market fluctuations.
TMGM offers low spreads, flexible leverage, and institutional-grade liquidity, ensuring fast execution and competitive trading conditions. Our advanced risk management tools, such as stop-loss and take-profit orders, help traders manage their positions effectively, while our secure trading environment provides confidence and peace of mind.
Start trading Crypto CFDs with TMGM today and take advantage of a regulated, professional trading environment designed to help you succeed in the dynamic world of cryptocurrency trading.
Trade Smarter Today





Account
Account
Instantly