Trend Following

Trend following strategies aim to capitalize on sustained directional movements in asset prices. “The trend is your friend” is a commonly cited principle underlying this approach. Traders employ tools such as moving averages and trendlines to identify whether a market is trending upwards or downwards. In an uptrend, traders generally initiate long positions, whereas in a downtrend, they consider short positions. Stop-loss orders are placed below significant support levels for long trades and above resistance levels for short trades. To optimize profits while protecting gains, traders often use trailing stop-loss orders that adjust as the price moves favorably.
Breakout Trading
Breakout trading targets strong price moves following clear market consolidation. Traders identify key support and resistance levels or chart patterns to anticipate potential breakouts and exploit periods of increased volatility. Buy orders are placed when the price breaks above resistance, while sell orders are positioned below support. Initial stop-loss orders are set within the consolidation range to manage risk. Profit targets are typically based on the height of the pattern's or previous swing highs and lows to maximize returns.
Mean Reversion Strategies
Mean reversion strategies operate on the premise that asset prices and returns will eventually revert to their long-term average or “mean”. Traders utilize momentum indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Bollinger Bands to detect overbought or oversold conditions. Counter-trend positions are initiated when these indicators show divergence, signaling a potential reversal. Given that trends can sometimes persist unexpectedly, traders employ tight stop-loss orders to limit downside risk. Profit targets are generally set near historical average price levels or at the opposite Bollinger Band boundaries.
News and Event Trading

This approach is grounded in fundamental analysis, focusing on market reactions to economic data releases, central bank interest rate decisions, or corporate earnings reports. Traders identify high-impact events and evaluate potential market moves based on whether actual outcomes meet, exceed, or fall short of expectations. Due to the heightened volatility around such events, some traders employ options-based strategies to hedge risk exposure. Awareness of wider spreads and reduced liquidity during major announcements is essential, as price movements can be erratic.
Price Action Trading
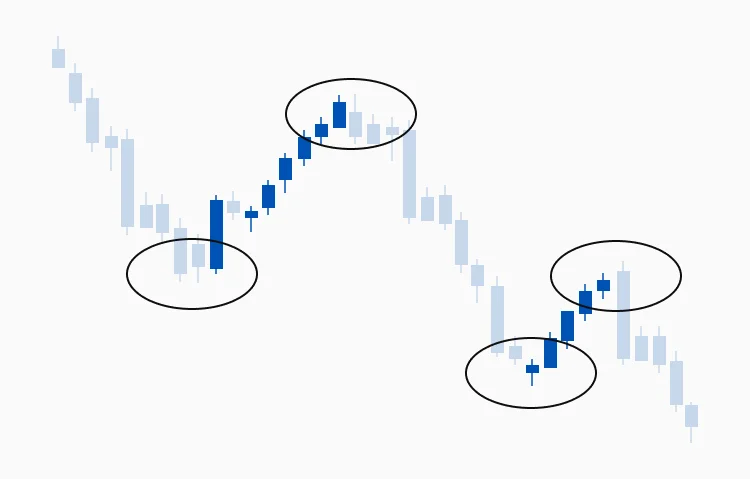
Price action traders rely on historical price movements displayed on charts to guide trading decisions, emphasizing raw price data rather than technical indicators like moving averages. This method involves analyzing candlestick patterns, support and resistance zones, and chart formations without heavy dependence on indicators. The focus is on interpreting market psychology and the behavior of buyers and sellers.
Price action trading is applicable across various timeframes and is most effective when combined with sound risk management practices.
Multi-Timeframe Analysis
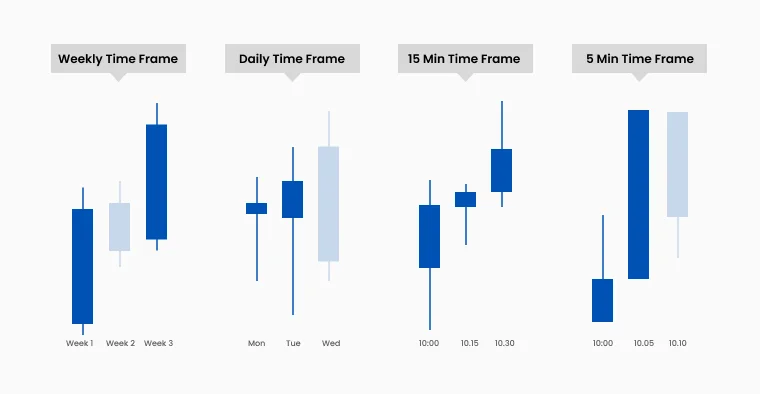
To enhance accuracy, many traders integrate price action with Multi-Timeframe Analysis. This involves using a higher timeframe to identify the prevailing trend, a medium timeframe to plan trade entries, and a lower timeframe to fine-tune execution. When signals align across multiple timeframes, it reduces conflicting data and strengthens trade setups.
Price action trading adapts well to diverse market conditions and timeframes. It is most effective when paired with disciplined risk management, including clearly defined stop-loss levels and appropriate position sizing.
Hedging Strategy
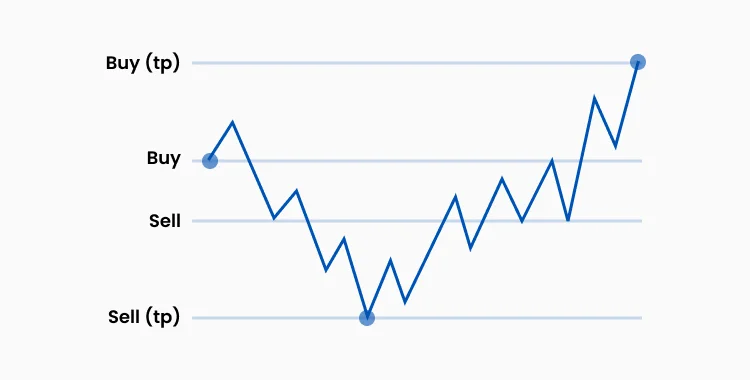
Hedging is employed to mitigate the risk of losses on an asset by opening an offsetting position. Traders use hedging during periods of market uncertainty or prior to significant news events. Hedging functions as an insurance mechanism for investments and typically involves derivatives such as options and futures contracts. However, hedging also limits potential profits and is not intended as a profit-maximizing strategy.
Scalping Strategy
This strategy entails executing numerous small trades throughout the trading day to profit from minor price fluctuations, often lasting seconds or minutes. It demands rapid execution, tight spreads, and strict discipline. Scalpers aim to accumulate a high volume of small profits, operating under the premise that micro price movements occur more frequently and are easier to capture than larger moves.
Scalping is suited for traders who prefer active, fast-paced trading but may not be ideal for beginners due to its intensity and speed.
Day Trading Strategy
Day trading is a high-risk, high-reward approach involving intraday buying and selling of securities to capitalize on small price movements while avoiding overnight exposure. Traders use momentum indicators, short-term chart patterns, and economic news calendars as key tools.
This strategy requires continuous market monitoring during active trading hours.
Swing Trading Strategy
Swing trading aims to capture short- to medium-term price movements lasting from several days to a few weeks. It performs well in smoothly trending markets. This strategy offers flexibility and suits part-time traders, providing a balance between the rapid pace of day trading and the longer-term holding periods of traditional investing.
Position Trading Strategy
Position trading focuses on capturing long-term market trends. It targets significant price moves over extended periods, typically weeks, months, or even years. Patience, a long-term outlook, filtering out short-term volatility noise, and emphasizing market sentiment are essential. Traders require a clear long-term perspective and often combine fundamental and technical analysis to determine optimal entry and exit points.
Risk Management Tips for CFD Trading
Position Sizing
Effective position sizing is a cornerstone of risk management, ensuring that no single trade disproportionately affects overall capital. A common guideline is to risk no more than 1–2% of trading capital on any individual trade. Position sizes should be calculated based on stop-loss levels to keep potential losses within acceptable boundaries.
Stop-Loss Placement
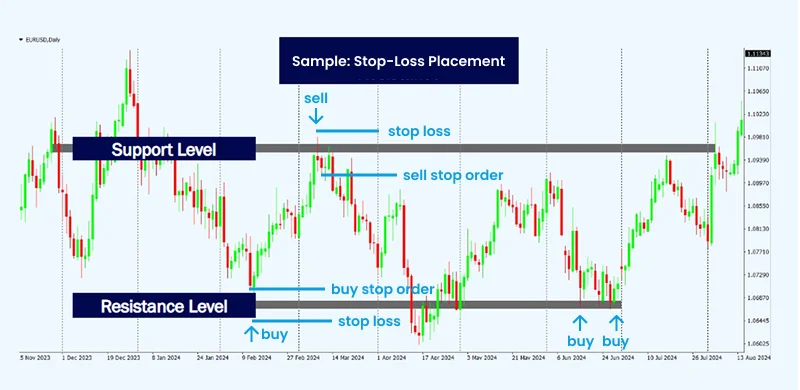
Strategic placement of stop-loss orders is vital to protect against unnecessary losses. Instead of arbitrary price distances, stops should be positioned at key technical levels such as support or resistance zones to minimize premature stop-outs. Factoring in market volatility when setting stop distances helps avoid exiting trades too early. For added protection, traders may use guaranteed stop-loss orders, especially during major economic releases, to limit risk from sudden price gaps or extreme volatility.
Risk-Reward Ratios
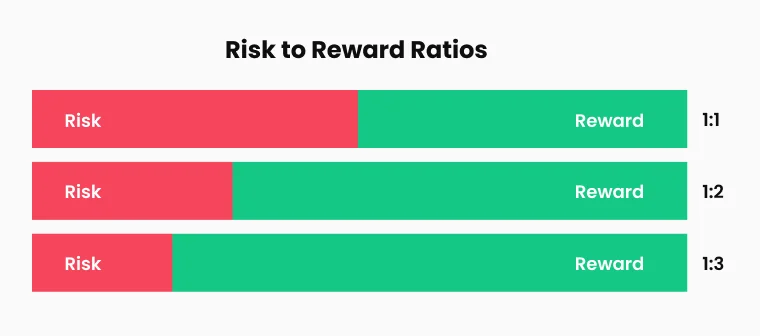
The risk-reward ratio is fundamental to long-term profitability. Traders typically target a minimum ratio of 1:2, meaning risking one unit of capital to potentially gain two. Higher ratios, such as 1:3 or above, allow traders to remain profitable even with lower win rates. Setting realistic profit targets aligned with current market conditions helps avoid holding positions for unrealistic gains. Some traders implement partial position exits to lock in profits on a portion of the trade while letting the remainder run for larger moves.
Correlation Risk
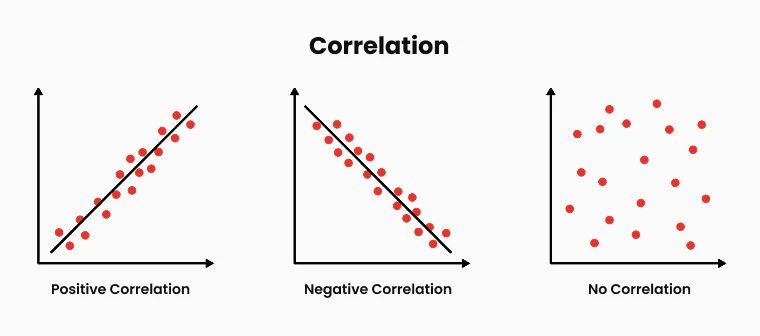
Managing correlation risk is essential to prevent excessive exposure to similar market drivers. Holding multiple positions in highly correlated assets can amplify risk, as price movements in one instrument may directly affect others. Understanding correlations between asset classes—such as forex pairs, commodities, and indices—aids in diversifying exposure. Monitoring overall portfolio delta exposure ensures directional risks remain balanced. Utilizing correlation matrices helps identify hidden relationships, avoiding unintended concentration of risk.
CFD Trading Tips for Beginners
CFD trading requires more than selecting the right strategies; it demands discipline, market awareness, and ongoing education. Here are key tips to improve your CFD trading performance:
Start with a Demo Account: Practice CFD trading on a demo account first. This enables you to familiarize yourself with trading platforms, test strategies, and understand market behavior without risking real capital.
Maintain Trading Discipline: Develop a detailed trading plan outlining entry and exit criteria, position sizing, and risk management rules. Adhere strictly to your plan to avoid impulsive decisions driven by emotions.
Use Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Always set predefined stop-loss and take-profit levels. These tools help manage risk effectively by limiting potential losses and securing profits when market conditions are favorable.
Stay Informed and Updated: Keep abreast of market news, economic indicators, and geopolitical developments that can significantly impact volatility. Use economic calendars to anticipate potential market-moving events.
Focus on Risk-Reward Ratios: Target favorable risk-to-reward ratios (at least 1:2 or higher) to ensure potential gains substantially exceed possible losses over time. This approach supports profitability even with moderate win rates.
Keep a Trading Journal: Record your trades, including the rationale behind each decision, market conditions, and outcomes. Regularly reviewing your journal helps identify successful patterns and areas for improvement.
Regularly Review and Adjust Strategies: Markets evolve, and previously successful strategies may require modification. Continuously evaluate your performance and adapt your strategies to remain effective in changing market environments.
By incorporating these practical tips into your CFD trading routine, you can enhance your market approach, improve decision-making, and achieve greater consistency and success in your trading activities.