What is Forex Trading and How Does It Work
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX, is the decentralized global marketplace where the world's currencies are exchanged. It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $9.6 trillion. Unlike stock markets, there is no central exchange; instead, forex trading is conducted electronically over-the-counter (OTC) between participants worldwide.
Key Takeaways
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week
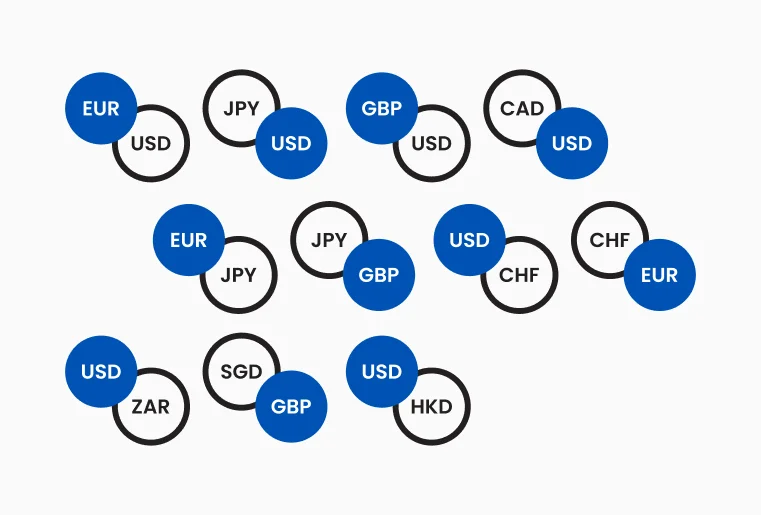
Currencies always trade in pairs (e.g. EUR/USD); you are simultaneously buying one and selling another
In forex trading, you can profit from prices rising (going long) or prices falling (going short).
Leverage allows traders to control large market positions with a relatively small deposit of capital.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, is the simultaneous act of buying one currency and selling another. All forex trades happen in pairs, such as EUR/USD.
While some of this currency exchange happens for practical reasons, like international business or tourism, the vast majority of market activity is for speculation.
This means traders buy and sell currencies with the specific goal of profiting from changes in their exchange rates.
Real-World Example of Currency Exchange
To understand what is forex trading in simple terms, consider the standard currency exchange process. When you travel to Japan, you exchange your home currency (e.g. US Dollars) for Japanese Yen.
You have effectively participated in the forex market. You sold Dollars and bought Yen.
If you stay in Japan for a week and the value of the Yen rises against the Dollar while you are there, when you exchange your leftover Yen back to Dollars at the end of the trip, you will receive more Dollars than you started with, That difference is your profit.
Speculation vs Hedging
There are two primary motivations for participants in the forex market:
Hedging
Multinational corporations use forex hedging to protect themselves against unfavorable currency price changes that could hurt their business operations.
Speculation
Most retail traders engage in forex trading solely to make a profit from fluctuations in exchange rates.
How Does Forex Trading Work?

When you engage in forex trading as a speculator, you are essentially buying "shares" in a particular country's economy. You buy a currency based on the belief that its economy will strengthen relative to another country's economy.
Going Long vs. Going Short
One of the unique benefits of forex trading compared to traditional stock investing is the ease with which you can profit from falling prices.
Going Long
You buy a currency pair if you believe the first currency (base) will rise in value against the second currency.
Going Short
You sell a currency pair of believe the first currency will fall in value. This allows trader to potentially profit even during economic downturns
Step-by-Step Example of a Forex Trade
Let's walk through a practical example of how forex trading works using the EUR/USD pair.
1. Selection: You select EUR/USD at a price of 1.1000.
2. Analysis: You decide to Go Long (Buy)
3. Action: You buy 1 Standard Lot (100,000 units)
4. The Result: The price rises to 1.1050 (50pips)
5. The Profit: The price moved 50 "pips" in your favor. On a standard lot, this equates to a profit of approximately $500.
Forex Trading Terminology: Pairs, Spreads, and Pips
To fully grasp what is forex trading, you must understand the key terminology and mechanics that define every transaction.
What are Currency Pairs?
In forex trading, currencies are always quoted in pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY, also known as forex pairs. This is because in every foreign exchange transaction, you are simultaneously buying one currency and selling another.
Base Currency
The first currency listed in the pair (e.g. EUR/USD). This is the currency you are buying are selling.
Quote Currency
The second currency listed (e.g. EUR/USD). This tells you how much of this currency is needed to but one unit of the base currency.
The most frequently traded pairs are known as the "Majors," and they always include the US Dollar (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY).
What is Spread in Forex?
When you look at a forex quote, you will see two prices: Bid Price (the price you sell at) and Ask Price (the price you buy at).
The difference between these two prices is called the Spread. This is essentially the transaction cost paid to the broker for facilitating the trade
What is a Pip in Forex?

A pip in forex stands for Percentage in Point. It is the standardized unit of measure for price movement in forex trading.
For most currency pairs, a pip is the fourth decimal place (0.0001). The notable exceptions are Japanese Yen Pairs, where a pip is the second decimal place (0.01).
For example, if EUR/USD moves from 1.2000 to 1.2001, it has moved one pip. Pipettes (or fractional pips) represent a 1/10 of a pip and are shown as the fifth decimal place in most currency pairs.
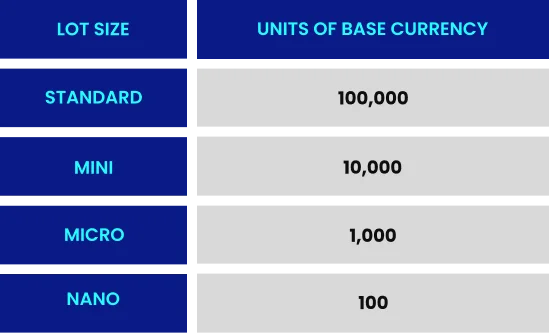
What is a Lot in Forex Trading?

In forex trading, a lot refers to the standardized unit of measurement for trade size, with one standard lot equal to 100,000 units of the base currency. The size of the lot directly impacts the value of a pip. For a standard lot of EUR/USD, each pip movement represents a $10 change in value.
Calculating Profit and Loss
To calculate potential profit or loss in forex trading:For a long position (buying): Profit/Loss = (Closing Price - Opening Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
For a short position (selling): Profit/Loss = (Opening Price - Closing Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
Example Calculation
Trading scenario:
Currency pair: EUR/USD
Opening position: Buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units) at 1.2000
Closing position: Sell at 1.2050
Calculation: (1.2050 - 1.2000) × 100,000 = $500 profit
What is Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading?
This is perhaps the most critical concept for beginners asking "what is forex trading?"
What is Leverage in Forex?
Leverage is essentially "borrowed capital" provided by your forex broker to increase the potential return of an investment. For example, with 30:1 leverage, you can control a $30,000 market position with only $1,000 of your own money.
What is Margin in Forex Trading?
Margin in forex is the actual capital you are required to deposit and maintain in your account to keep that leverage position open.
Leverage is a double-edged sword:
- It magnifies potential profits from favorable market movements
- It equally magnifies potential losses from adverse market movements
Risk Management with Leverage
- Position Sizing: To mitigate excessive exposure, limit each trade to a small percentage of your total capital. A commonly recommended approach is risking no more than 1-2% per trade.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Always use stop-loss orders to define the maximum acceptable loss for each trade, ensuring that sudden market movements do not lead to significant capital drawdowns.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Prioritize trades with a favorable risk-reward ratio, typically aiming for at least 1:2. This ensures that successful trades can offset potential losses over time.
- Leverage Reduction: While brokers may offer high leverage, consider using less than the maximum available to reduce risk exposure and prevent unnecessary liquidation.
- Stress Testing: Assess how different market conditions, including high volatility, may impact leveraged positions. This helps forex traders prepare for unexpected price fluctuations and adjust strategies accordingly.
Effective leverage management ensures controlled risk exposure and long-term sustainability in trading.
Forex Market Participants and Trading Sessions
The forex market is a vast ecosystem with various participants operating across time zones.
Who are the Main Forex Market Participants?
The market is composed of a hierarchy of participants:
Central Banks & Commercial Banks
They trade billions daily in the "Interbank Market"
Hedge Funds & Corporations
Large Institutions trading for speculation or hedging needs.
Retail Forex Traders
Individuals accessing the market via online forex brokers
Forex Market Hours and Sessions
A key aspect of forex trading is its 24-hour nature.
The most active times to trade are usually when major sessions overlap (London/ New York Overlap) as liquidity is as its highest.
The 4 sessions across different forex market hours are: Sydney, Tokyo, London, New York.
Pros and Cons of Forex Trading
Before starting, it is vital to weigh the benefits against the risks.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High Liquidity: Easy to enter and exit trades instantly. | High Risk: Leverage can lead to significant losses rapidly. |
| 24/5 Accessibility: Trade on your own schedule during the week. | Volatility: Sudden news events can cause sharp price spikes. |
| Low Transaction Costs: Spreads are generally lower than stock commissions. | Complexity: Requires understanding macroeconomics and technical analysis. |
| Profit in Any Direction: Ability to short sell in falling markets. | Emotional Stress: Fast paced markets can be psychologically challenging. |
How to Start Forex Trading with TMGM
TMGM If you are ready to begin your journey into forex trading, follow these steps with a regulated forex broker like TMGM.
1. Continue Your Education: Read through the resources in the TMGM Trading Academy to deepen your knowledge.
2. Practice Risk-Free: Open a TMGM Demo Account.
3. Choose a Reliable Broker: Ensure that your broker is regulated (like TMGM is by ASIC) and offers competitive spreads.
4. Start Live Trading Small: When you are ready to trade real capital, start with Micro Lots.
Trade Smarter Today




Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Forex (FX) Trading mean?
Is there a difference between forex trading and currency trading?
How can I make money from forex trading?
How can I get started trading forex?
What costs and fees do you have to pay when trading forex?

Account
Account
Instantly