

What is Spread in Forex and How to Calculate it
The difference between a currency pair's asking (buy) and bid (sell) prices is known as a spread. There are always two prices for all currency pairs at any given time: the bid and the asking price. The asking price is the amount you would pay to purchase the base currency, and the bid price is the price you sell it. If this sounds confusing, don't worry - you're not alone. Many new traders struggle to grasp this concept, yet understanding spreads is fundamental to successful forex trading. Let's break it down into simple terms and explore why it matters in your trading journey.
Key Takeaways
The spread is the ask price minus the bid price for a pair. It is quoted in pips. Tight spreads mean lower trading costs and usually appear when liquidity is high, while wide spreads often signal thin liquidity or elevated volatility.
Calculation is simple. Example: GBP USD quoted at 1.3089 and 1.3091 has a spread of 0.0002 which equals two pips. Most pairs use the fourth decimal as one pip, but JPY pairs use the second decimal.
Spreads can be variable or fixed. Variable spreads move with market conditions, while fixed spreads stay constant regardless of short term swings.
Spreads widen with volatility and low liquidity and tend to narrow during major market sessions such as London and New York, especially during overlaps. Majors usually have tighter spreads than exotics.
Managing spread risk matters. Wider spreads raise costs and can contribute to margin calls or even liquidation. Control position size and leverage, use tools like spread indicators and an economic calendar, and practice on a demo with a regulated low spread broker.
What Is Spread in Forex?
In forex trading, the spread is the difference between the bid price (what buyers are willing to pay) and the ask price (what sellers are asking) for a currency pair. It represents the cost of entering a trade and is measured in pips. A tighter (low) spread means lower trading costs and often occurs during high-liquidity periods, while a wider spread indicates higher costs and may signal low liquidity or increased market volatility. Understanding how spreads work is key to choosing a low spread forex broker and managing overall trading expenses.
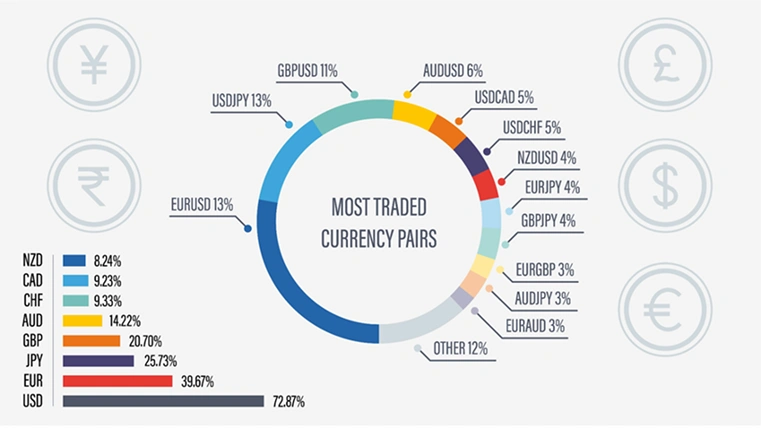 Here is a list of the more popular Forex pairs:
Here is a list of the more popular Forex pairs:
USD/JPY: US dollar and Japanese yen
EUR/USD: Euro and US dollar
USD/CHF: US dollar and Swiss Franc
GBP/USD: British pound and US dollar
Forex Trading Pip Spread

In forex trading, the spread is measured in pips, which represent a small movement in the price of a currency pair and are typically the last decimal place in the price quote (0.0001). This applies to most currency pairs, except for the Japanese yen, where a pip is measured at the second decimal place (0.01).
A wider spread indicates a larger difference between the two prices, often signaling low liquidity and high volatility. Conversely, a narrower spread suggests low volatility and high liquidity. As a result, trading a currency pair with a tighter spread incurs lower spread costs, making it more cost-effective for forex traders.
When trading forex, the spread can be either variable or fixed. A variable spread fluctuates as the bid and ask prices of the currency pair change, while a fixed spread remains constant.
How to Calculate Spread in Forex?
To calculate spread in forex, deduct the asking price from the bid price. For instance, the spread on a trade of GBP/USD at 1.3089/1.3091 equals 1.3091 – 1.3089, or 0.0002 (2 pip). Spreads can be tight (low) or broad (high); the greater the spread, the more pips are obtained from the formula above.
Within a price quote, the spread is calculated using the most recent large numbers of the buy and sell prices. You pay the full spread upfront when trading forex or any other asset through a spread betting or CFD trading account.
In contrast, when trading share CFDs, a commission is paid when a trade is entered and exited. As a trader, you receive better value the tighter the spread is.
Before trading in the forex market, you can try a risk-free method by creating a demo account with virtual funds.
What Causes High Spread in Forex? 
Market volatility is one factor that might affect the forex spread and lead to fluctuations. Significant economic factors have the power to enhance or weaken a currency pair, which in turn influences the spread. Currency pairs may gap or become less liquid in a volatile market, which will cause the spread to increase.
Watching our economic calendar can help you be ready for the potential for larger spreads. You can forecast if currency pairs' volatility will rise and, consequently, whether you will notice a wider spread by keeping up to date on the events that could make them less liquid. However, planning for unexpected economic data or breaking news can be hard.
Lower spreads are usually observed during the main forex market sessions, which take place in London, New York, and Sydney. The spread can be even more constrained when there is an overlap, such as when the London session is concluding and the New York session is starting. The overall supply and demand of currencies also affect the spread; if a strong demand for the euro, its value will rise.
Using Spread in Forex Trading Strategies
Forex traders can use an event-driven approach based on macroeconomic indicators to trade the tightest spreads and take advantage of favorable times. For instance, forex traders can anticipate changes in the forex market and identify appropriate entry and exit opportunities when initiating a position by keeping an eye on the most recent trading news and economic updates. We refer to this as event-driven trading.
Are you keen on trading with the best currency pairs in the Forex market? Check out our list of recommended currencies here.
Forex Spread Indicator
Using a trading indicator is another way to improve a forex spread strategy. When displaying the direction of the spread to the bid and ask prices, the forex spread indicator is usually represented as a curve on a graph. With the most liquid pairs having tighter spreads and the more exotic pairs having broader spreads, this visualizes the spread in the forex pair over time.
Additionally, there will be a smaller spread for currency pairs traded in large quantities, such as big pairs that include the USD. Despite the enhanced liquidity of these pairings, spreads could nevertheless expand in the event of economic instability.
Forex Spread Changes and Risk Mitigation
You may be subject to a margin call or, in the worst-case scenario, liquidation if the forex spread expands significantly. When your account value falls below 100% of your margin level, a margin call message is sent to you, alerting you to the possibility that you may not be able to meet the trading requirement. You risk having all your holdings liquidated if you drop 50% below the margin level.
Determining your position's size and the leverage you are using while trading forex is crucial. Since shares are typically exchanged in smaller increments than forex pairs, keeping track of your account balance is critical.
Low Spread Forex Broker
The difference between a currency pair's asking and bid prices is known as a forex spread, typically expressed in pip amounts. When trading forex, it is important to understand what causes the spread to grow.
Exotic currency pairs will spread more than major ones, as the former are traded in higher volumes. Looking for the best forex broker? Why not register for a TMGM account now and explore the trading markets?
The difference between a currency pair's asking and bid prices is known as a forex spread and is typically expressed in pip amounts. When trading forex, it is important to understand what causes the spread to grow. Exotic currency pairs will spread more than major currency pairs because the former are traded in higher volumes. You should manage your finances and risks when trading in the forex market.
Trade Smarter Today




Frequently Asked Questions
What is the spread in forex?
How do I calculate the spread and its cash cost?
Why do spreads change during the day?
What is the difference between fixed and variable spreads?
Does a lower spread always mean a lower total cost?

Account
Account
Instantly




