

Trading Styles: Scalping vs Day Trading vs Swing Trading
The world of financial markets is dynamic, with diverse strategies available to traders. Three of the most popular trading styles—scalping, day trading, and swing trading—differ significantly in terms of execution speed, time commitment, and risk tolerance. Each method offers unique advantages and challenges, making it essential for traders to select a trading strategy that aligns with their goals, risk appetite, and time constraints. By understanding the intricacies of each style, traders can make more informed decisions and optimize their chances of success.
Understanding Scalping
Scalping is one of the fastest-paced day trading strategies. It involves high-frequency trades designed to capture small price fluctuations within seconds or minutes. It requires a meticulous approach and relies heavily on technical indicators, chart patterns, and market order flows.
Key Components of Scalping
Short Timeframes: Scalpers typically use 1-minute, 3-minute, or 5-minute charts to make quick, precise trades. These charts offer a zoomed-in view of price action, highlighting micro-level movements.
Key Indicators: RSI (Relative Strength Index), Stochastic Oscillators, and Bollinger Bands are essential for scalpers to assess momentum and overbought/oversold conditions. Moving averages (MA), particularly the Exponential Moving Average (EMA), are also heavily relied upon to identify short-term trends.
Market Liquidity: Scalpers thrive in highly liquid markets, where the bid-ask spread is narrow, ensuring they can execute trades with minimal slippage. Currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD are popular among scalpers for their liquidity.
Example Strategy: A scalper might enter a trade when the price moves outside the upper or lower Bollinger Band (indicating overbought/oversold conditions) and exit after a small profit when the price returns to the moving average.
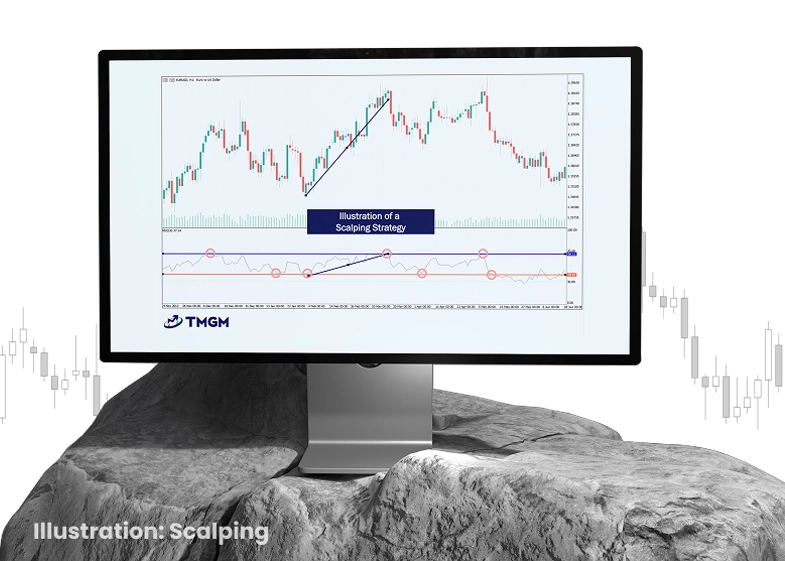
Pros and Cons of Scalping
Pros:
Frequent Profit Opportunities: The high frequency of trades creates more chances for small profits throughout the day.
Minimal Exposure to Market Risk: Scalping avoids long-term market risk as positions are held for a very short time.
Cons:
Stressful & Time-Consuming: Scalping requires constant focus, making it mentally exhausting.
Infrastructure Demands: Traders must invest in advanced trading technology, including fast internet connections, to prevent execution delays, which can hurt profitability.
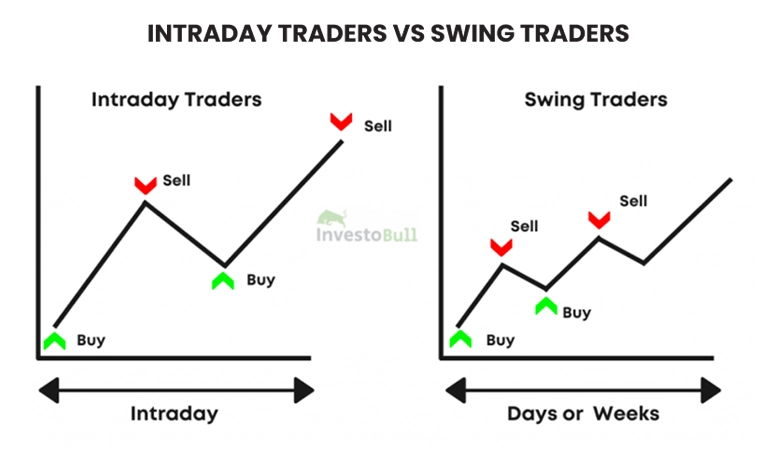
The Mechanics of Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling assets within the same trading session. Unlike scalping, day traders hold positions for hours or even minutes, capitalizing on price fluctuations that occur during market hours.
Key Components of Day Trading
Chart Timeframes: Day traders typically use 15-minute, 30-minute, and 1-hour charts to track intraday price action. These timeframes strike a balance between scalping's micro-focus and swing trading's longer-term perspective.
Indicators & Tools: Day traders rely on a wide range of indicators, including Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Fibonacci retracements, pivot points, and volume analysis. These tools help traders gauge market momentum, identify potential reversals, and assess overall price strength.
Trade Duration: While positions are held for longer than in scalping, day traders still close their trades before the market closes, thereby avoiding overnight risks. They typically aim for price moves ranging from 0.5% to 2% within the trading day.
Example Strategy: A day trader may use Fibonacci retracements to identify areas where price might reverse during an intraday correction. Combining this with moving average crossovers (e.g., 9-period and 21-period moving averages) can help signal the best entry and exit points.
Pros and Cons of Day Trading
Pros:
Profit Potential per Trade: With larger price moves, day traders have the chance for more substantial profits per trade compared to scalpers.
No Overnight Exposure: Positions are closed before the market closes, eliminating the risks of overnight price gaps.
Cons:
Requires Full-Time Attention: Day trading necessitates constant market monitoring, which can be difficult for those with limited time availability.
Psychological Pressure: The fast pace and volatility of intraday movements can lead to emotional stress and impulsive decisions if a trader does not have the right mindset.
Exploring Swing Trading
Swing trading offers a medium-term approach. Traders typically hold positions for several days to weeks, aiming to profit from market trends that span a longer time frame than those targeted by scalpers and day traders. Swing traders seek to capture "swings" in the market, which are price movements within a larger trend.
Key Components of Swing Trading
Chart Timeframes: Swing traders use daily, 4-hour, and 1-hour charts to assess price action over several days. These charts offer a broader perspective of the market's movement compared to the tighter timeframes used in scalping and day trading.
Indicators & Tools: Swing traders commonly use trend-following indicators such as moving averages (like the 50-day moving average), RSI, Bollinger Bands, and MACD to identify trends and entry points.
Risk Management: Swing traders often employ larger stop-loss levels, giving the market more room to "breathe" during periods of consolidation or retracement. This provides more flexibility compared to scalping or day trading.
Example Strategy: A swing trader might enter when the price rebounds from a key support level or when the market shows signs of forming a new trend. They may exit when the price approaches resistance levels or after a predetermined profit target is met.
Pros and Cons of Swing Trading
Pros:
Potential for Larger Profits per Trade: Swing trading allows traders to capture larger price movements, yielding potentially more significant profits compared to scalping or day trading.
Less Time-Intensive: Since positions are held over several days or weeks, swing traders do not need to monitor the markets constantly.
Cons:
Overnight Risk: Swing traders are exposed to overnight market risks as positions are held through market closures.
Capital Requirements: Due to longer holding periods, swing traders often require more capital to manage positions and withstand adverse price movements.
Choosing the Right Trading Style
Selecting the right trading style involves considering several factors:
Time Commitment: Scalping demands full attention throughout the day, while day trading requires focus during trading hours. Swing trading is more flexible, as positions can be monitored less frequently.
Risk Tolerance: Scalping and day trading expose traders to higher levels of volatility, while swing trading allows more room for strategic adjustments.
Personality & Psychological Factors: Scalpers often need a high degree of discipline and focus, while day traders may experience heightened stress due to constant market fluctuations. Swing traders need patience to allow positions to develop and mature.

Essential Tips for Trading Success
Scalping Tips
Invest in Speed: High-frequency trading requires low-latency setups and fast execution. Prioritize platforms with direct market access (DMA) to minimize slippage.
Master Technical Patterns: Scalpers must understand candlestick formations, price action patterns, and short-term chart patterns like double tops or head-and-shoulders.
Risk Management: Due to the large volume of trades, it’s essential to use tight stop losses and a favorable risk-to-reward ratio on each trade.
Day Trading Tips
Use Multiple Indicators: Combining technical indicators like MACD with fundamental news (e.g., earnings reports, and economic data releases) allows day traders to make informed decisions.
Develop a Trading Plan: A detailed plan, including stop-loss levels, take-profit targets, and entry criteria, is essential to reduce emotional trading.
Stay Disciplined: Avoid impulsive decisions based on short-term market noise. Stick to your strategy, and don’t chase the market.
Swing Trading Tips
Identify Strong Trends: Use moving averages to identify long-term trends and enter positions when the price pulls back to a key level within the trend.
Manage Risk: Utilize trailing stops to protect profits and prevent large losses as the market moves in your favor.
Be Patient: Swing traders must wait for the market to show clear signals of direction before entering, which may require holding cash positions for extended periods.

Each trading style—scalping, day trading, and swing trading—has unique advantages and challenges. By gaining a deep understanding of scalping, day trading, and swing trading, traders can make informed decisions based on their personal goals and resources.
Success in trading requires mastering both the technical and psychological aspects of the game and maintaining a solid risk management plan. The right approach depends on a trader’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and availability.
No matter the style, trading success requires thorough research, disciplined execution, and a well-defined risk management strategy. Understanding market dynamics and continuously improving trading skills can significantly enhance profitability.
Trading with TMGM: The Perfect Platform for Scalpers, Day Traders and Swing Traders
Whether you’re inclined toward the fast pace of scalping, the highs and lows of swing trading or the strategic rhythm of day trading, TMGM provides a robust trading environment for all approaches. With access to advanced tools on MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5, TMGM offers competitive spreads, high-leverage options, and efficient order execution to support quick entries and exits.
Start Trading with TMGM Today! Maximize your trading potential with TMGM’s cutting-edge platform, low spreads, and advanced risk management tools. Whether you prefer scalping, day trading or swing trading, TMGM provides the resources and support you need to succeed in global markets. Sign up now and take your trading to the next level!
Trade Smarter Today





Account
Account
Instantly




