
How to Invest in Precious Metals: A Complete Guide
Precious metals, especially gold and silver, are a lucrative investment market that attracts investors worldwide. Many new traders are especially interested in understanding how to invest in gold and silver. This complete guide explains the fundamentals of investing in precious metals.
What are Precious Metals?
Precious metals are natural resources with high economic and industrial value. They are considered valuable due to scarcity, strong demand.
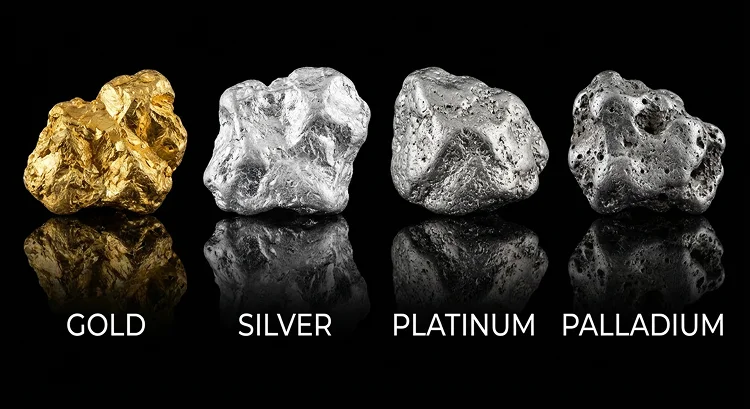

Eight types of metals fall into this category: gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium, and osmium. Many modern traders focus on understanding how to invest in gold and silver because these two metals dominate global demand and are widely used in jewellery, technology, and investment portfolios.
Why Trade Precious Metals?
Precious metals trading provides many benefits. They are a strategic method to hedge against inflation. Gold and silver attract higher demand when interest rates are low.
Another benefit is the consistent demand from many central banks that help support market prices, maintaining it as a strong long-term asset. These metals also provide safety during political conflicts, recessions, natural disasters, and periods of financial stress. Investing in precious metals also helps diversify portfolios, which can reduce risk because these assets often behave differently from equities or currency markets.
Risks of Trading Precious Metals
However, like all trades, there are risks associated with precious metal trading. They can experience strong price volatility. Market conditions can change quickly due to global events, industrial demand, and investor sentiment.
Industrial demand can also impact silver more than gold, which is why the topic of gold vs silver is important for traders comparing long-term potential and risk levels. Regulatory changes can affect mining operations, international trade, and the environmental rules that influence production.
What Affects Precious Metal Prices?
Demand and supply. Higher demand or even the expectation of higher demand raises metal prices; on the other hand, high supply lowers metal prices.
The performance of the US Dollar (USD). Because precious metals are traded in USD, the price of precious metals can increase if the currency falls. The opposite is also true.
Interest rates and monetary policies. When interest rates are lower and monetary policies are less strict, the price of precious metals is expected to increase due to potential inflation and lower yields on other assets.
Economic data. A weak global economy can increase demand for precious metals, especially safer ones like gold.
Political risk. Uncertainty in a country’s politics will repel potential investors. In regions where precious metals are mined, this could also affect supply chains and increase prices.
Precious Metals Investment Options
Choosing the type of precious metals asset class is the next important step as you learn how to invest in gold and silver:
Physical ownership
Physically purchasing precious metals allows for physical ownership, but there can be high selling, buying, and storage fees as precious metals must be kept securely. The exact amount also cannot be selected for investment, as you need to buy the weight of a full gold bar or coin.
Buying and selling also occur within specific time frames, which could limit trade. That is why many modern traders prefer gold CFD trading.
Shares
Buying shares of companies that extract precious metals is also a great option. Some of the largest mining companies include Barrick Gold and Newmont Mining. This option offers many advantages, including high liquidity, lower fees and commissions, portfolio diversification, lower initial investments, and passive income from dividends.
Although shares track the performance of precious metals indirectly, the price of a company stock may not always reflect the real movement of gold or silver.
Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)
An ETF allows traders to invest in gold, silver, or mining companies through a single market instrument. ETFs are bought and sold like individual stocks and provide convenient exposure to a wide basket of assets. They offer portfolio diversification, high liquidity, and lower storage costs compared to physical holdings. Traders should note that some ETFs track specific prices differently from the actual movement of underlying metals.
Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
Gold CFD trading is one of the most flexible ways to take part in the metal markets. A CFD is an agreement to exchange the difference in price between the opening and closing of a trade. This method allows traders to speculate on upward or downward movements without owning gold or silver directly. CFDs provide the opportunity to trade with leverage, access global markets quickly, and gain exposure at lower initial capital. Traders can also enter short positions when they expect prices to fall.
Futures contracts
Futures contracts involve an agreement to buy or deliver a commodity at a specific date. These contracts offer strong liquidity and flexible trading hours. Futures require higher initial capi,tal and involve expiry dates, making them more suitable for experienced traders who can manage margin requirements.
How to Start Trading Precious Metals
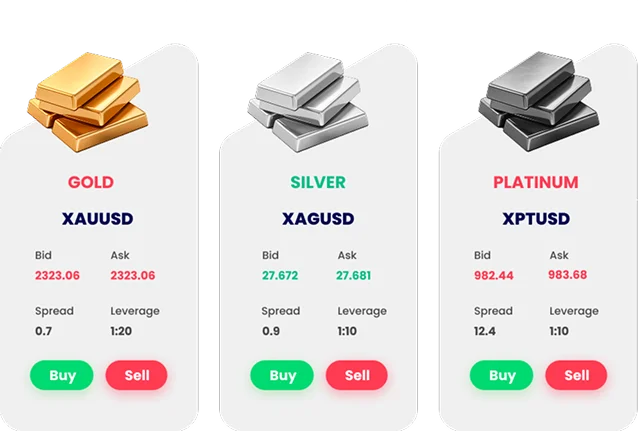
Trading Platforms such as TMGM allow traders to trade the most popular precious metals at exceptionally tight pricing. TMGM offers leverage of up to 1:1000 and consistently helps traders achieve the best spreads.
Beginners who want to learn how to invest in gold and silver can start with a demo account, trading precious metals can be achieved through a few simple steps:
Choose your account.
Download a trading platform.
Choose from the most popular precious metals .
Make your first trade.
Trade Smarter Today




FAQ About Investing In Precious Metals
What should I learn to begin to invest in gold and silver?
How does gold CFD trading work?
How should traders compare gold vs silver investment?

Account
Account
Instantly





