Key Takeaways
Forex (FX) is a 24-hour, five-day over-the-counter market where currencies are traded in pairs (e.g., EUR/USD), with a daily turnover exceeding 9.6 trillion US dollars.
Each quote represents the price of one unit of the base currency in terms of the quote currency; the bid-ask spread constitutes a primary trading cost.
Price fluctuations are measured in pips (0.0001 for most pairs, 0.01 for JPY pairs), and the lot size determines the pip value and overall profit or loss.
Traders can take long or short positions, and leverage allows control of larger positions but also amplifies losses, making position sizing and stop-loss orders essential.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, involves simultaneously buying one currency and selling another, aiming to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. All forex trades occur in pairs, such as EUR/USD.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with forex market hours spanning major financial centers such as London, New York, and Tokyo, and daily trading volume exceeding $9.6 trillion.
How Does Forex Trading Work?
Forex trading functions like any financial exchange where one asset is swapped for another, typically conducted via online platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4).
In this context, forex traders buy one currency while simultaneously selling another. The market price of a currency pair indicates how much of the quote currency is required to purchase one unit of the base currency.
For example, if the GBP/USD pair is quoted at 1.2500, it means 1 British pound is equivalent to 1.25 US dollars.
Each currency is identified by a three-letter ISO code, facilitating efficient trade execution. Below are some common currency codes:
- USD – US Dollar
- EUR – Euro
- GBP – British Pound
- JPY – Japanese Yen
- AUD – Australian Dollar
These codes enable traders to quickly identify and execute currency pair trades efficiently.
Figure 1 : Illustrates different unique currency codes
Forex Trading Fundamentals
What are Currency Pairs?
A currency pair, also called a forex pair, is the quotation of two different currencies, with the first currency listed as the base and the second as the quote. The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
For example, in the pair EUR/USD, the euro is the base currency and the US dollar is the quote currency, meaning you need a certain amount of US dollars to purchase one euro.
What are Major Currency Pairs?
Major currency pairs are the most actively traded pairs in the forex market, all of which include the US dollar (USD).
They are characterized by high liquidity, tight spreads, and significant trading volume. The seven primary pairs are EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, USD/CAD, USD/CHF, and NZD/USD.
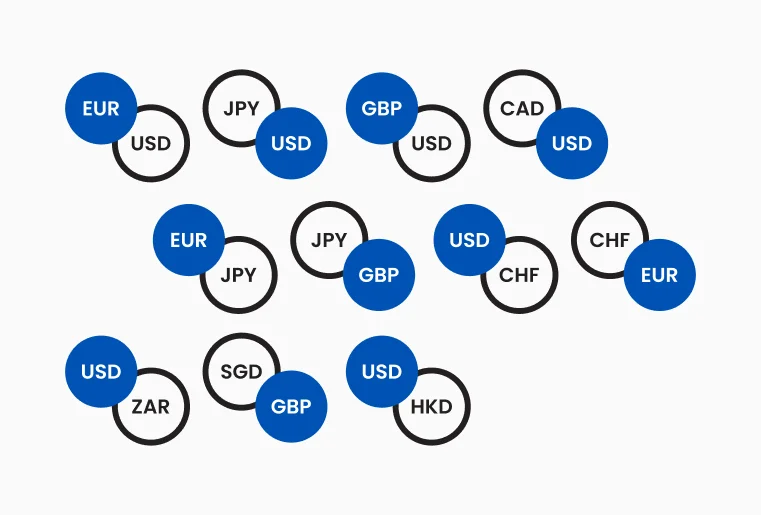
Figure 2: Illustrates major currency pairs
Minor and Exotic Pairs
- Minor pairs: Combinations of major currencies excluding USD (e.g., EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY)
- Exotic pairs: Combinations of a major currency with the currency of an emerging or smaller economy (e.g., USD/TRY, EUR/ZAR)
Understanding Currency Pair Quotes
Each currency pair quote includes two prices:
- Bid price: The price at which you can sell the base currency
- Ask price: The price at which you can buy the base currency
The difference between these prices is called the spread, representing one of the main transaction costs in forex trading.
Base and Quote Currencies

Figure 3: Illustrates Base and Quote Currencies
In the currency pair EUR/USD:
- EUR is the base currency
- USD is the quote currency
The exchange rate indicates how much of the quoted currency (USD) is required to purchase one unit of the base currency (EUR). For example, if EUR/USD is quoted at 1.2000, one euro can be exchanged for 1.20 US dollars.
What are Pips and Lots in Forex?

Figure 4: Illustrates One Pip
What is a Pip in Forex?
A forex pip (percentage in point) is the smallest standardized price increment in forex trading:
- For most currency pairs: a 0.0001 change in price (fourth decimal place)
- For pairs involving the Japanese yen: a 0.01 change in price (second decimal place)
For example, if EUR/USD moves from 1.2000 to 1.2001, it has moved one pip. Pipettes (fractional pips) represent one-tenth of a pip and are displayed as the fifth decimal place in most currency pairs.
How to Calculate Pips in Forex?
To calculate pips, find the difference between two price levels. In most currency pairs, the fourth decimal place represents one pip. For pairs where USD is the quote currency (e.g., EUR/USD), pip value is calculated by multiplying the lot size by 0.0001.
For pairs where USD is the base currency (e.g., USD/EUR), divide 0.0001 by the current exchange rate, then multiply by the lot size.
Example of Pip Value Calculation for a Standard Lot
Currency Pair Example: EUR/USD
Position Size: 1 standard lot = 100,000 EUR
Exchange Rate= 1.2000
One Pip Movement (0.0001)= 100,000 X 0.0001 = US$10
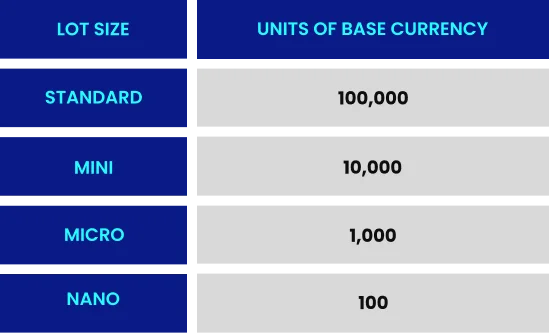
If you trade a mini lot (10,000 units), one pip equals US$1.
If you trade a micro lot (1,000 units), one pip equals US$0.10
What is a Lot in Forex Trading?

Figure 5: Illustrates One Lot
In forex trading, a lot refers to the standardized unit size of a trade, with one standard lot equaling 100,000 units of the base currency. The lot size directly affects the pip value. For a standard lot of EUR/USD, each pip movement corresponds to a $10 change in value.
Calculating Profit and Loss
To calculate potential profit or loss in forex trading:For a long position (buy): Profit/Loss = (Closing Price - Opening Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
For a short position (sell): Profit/Loss = (Opening Price - Closing Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
Example Calculation
Trading scenario:
Currency pair: EUR/USD
Opening position: Buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units) at 1.2000
Closing position: Sell at 1.2050
Calculation: (1.2050 - 1.2000) × 100,000 = $500 profit
What is a Forex Trader?
A forex trader is an individual or institution that participates in the forex market by buying and selling currency pairs, aiming to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. Traders can be retail clients or institutional entities such as banks and hedge funds.
How to Become a Forex Trader?
Key steps to becoming a forex trader include:
1. Learn the fundamentals
Research, study, and understand core forex concepts such as currency pairs, pips, lots, spreads, leverage, margin, and market mechanics. TMGM’’s Trading Academy offers comprehensive coverage of these topics.
2. Choose a reputable trading broker
To trade forex online, you need a broker. Ensure the broker is regulated, licensed, and transparent about fees. TMGM meets these standards.
3. Open and set up a trading account
Begin with a demo account funded with virtual capital to practice trading without risking real money. TMGM offers a demo account that allows trading real forex pairs risk-free.
4. Start trading with smaller lot sizes and scale up
Once ready, trade with small lot sizes to limit risk and avoid high leverage initially. Increase trade size as confidence and skill improve.
5. Continue learning about forex trading
Stay updated on market news, economic releases, central bank announcements, and refine your trading strategy over time.
What is Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading?
What is Leverage in Forex?
Leverage enables forex traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. It is expressed as a ratio, such as 30:1, meaning you can control a position 30 times the size of your invested capital.
Leverage is a double-edged sword:
- It amplifies potential profits from favorable market moves
- It also amplifies potential losses from adverse market moves
What is Margin in Forex Trading?
Margin in forex is the collateral deposit required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It serves as security for the leveraged exposure.
Types of Margin
- Initial Margin: The percentage of the total trade value required to open a position. For example, with 30:1 leverage, the initial margin requirement is approximately 3.33% of the position size.
- Maintenance Margin: The minimum account equity required to keep a position open. If equity falls below this due to losses, a margin call may be issued requiring additional funds, or positions may be liquidated (stopped out).
How to Calculate Margin in Forex Trading
For a EUR/USD trade with:
- Position size: 1 standard lot (100,000 EUR)
- Current exchange rate: 1.2000
- Position value in USD: 120,000
- Leverage: 30:1
- Initial margin requirement: 120,000 ÷ 30 = $4,000
You need at least $4,000 in your account to open this position.
Risk Management with Leverage
Leverage can magnify both gains and losses, making risk management essential for sustainable trading.
- Position Sizing: Limit each trade to a small percentage of your total capital, commonly 1-2%, to avoid excessive exposure.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to cap maximum losses per trade, protecting capital from sudden adverse moves.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Target trades with a favorable risk-reward ratio, typically at least 1:2, so gains can offset losses over time.
- Leverage Reduction: Although brokers may offer high leverage, consider using lower leverage to reduce risk and avoid forced liquidation.
- Stress Testing: Evaluate how different market conditions, including volatility spikes, affect leveraged positions to prepare and adjust strategies.
Effective leverage management is key to controlling risk and ensuring long-term trading viability.
What is the Forex Market
Forex trading is decentralized and conducted over the counter (OTC). Instead of a centralized exchange, transactions occur electronically between banks, brokers, institutions, and retail traders.

Figure 6: Illustrates daily forex transactions
The Evolution of Forex Trading
The modern forex market has evolved significantly:
Pre-1970s: Fixed exchange rates under the Bretton Woods system
1971: Shift to floating exchange rates after Bretton Woods collapse
1980s-1990s: Introduction of electronic trading platforms and broader institutional access
Early 2000s: Rise of online retail forex brokers, expanding access to individual traders
Present day: Advanced algorithmic trading, mobile platforms, and integration with other asset classes
Today'’s forex market is a sophisticated ecosystem where central banks, commercial banks, investment firms, corporations, and retail traders continuously interact across global markets.
What Moves the Forex Market?
Economic Factors
Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a pivotal role in monetary policy, directly impacting currency values. Interest rate decisions are a primary tool.
Economic Indicators
Key economic data releases that influence forex markets include: 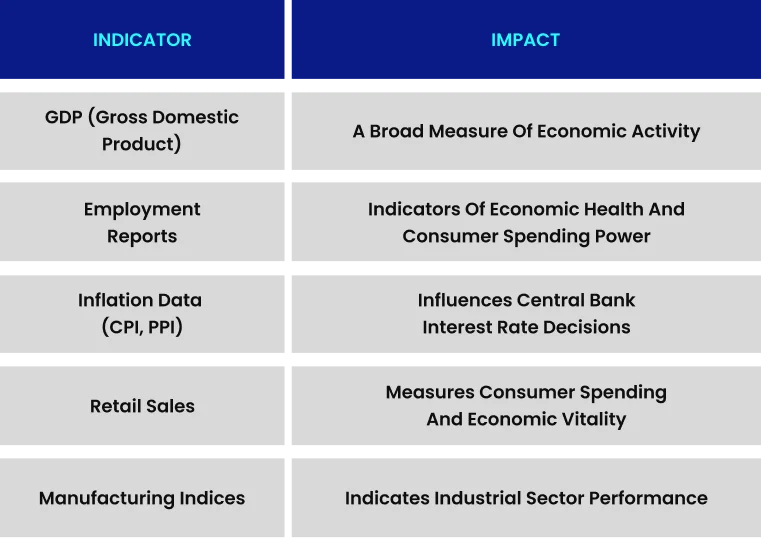
Geopolitical Events
- Elections: Political changes can signal policy shifts affecting currencies
- Trade Agreements/Disputes: Affect economic relations between countries
- Regional Conflicts: Create uncertainty and risk aversion
- Regulatory Changes: New financial regulations can influence capital flows
Market Psychology
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment reflects traders’ overall mood, influencing price movements beyond fundamentals. It plays a key role in short-term trends and momentum-driven markets.
Trade Forex with TMGM
TMGM is a leading forex broker offering superior trading conditions, advanced technology, and comprehensive support for traders at all levels.
Why Choose TMGM for Forex Trading
TMGM is a premier forex broker providing excellent trading conditions, cutting-edge technology, and full support for traders of all experience levels.
TMGM offers tight spreads starting from 0.0 pips on major currency pairs with competitive commissions. Traders can access leverage up to 1:1000, benefiting from deep liquidity aggregated from multiple tier-1 providers for efficient execution. The platform delivers fast execution speeds, averaging under 30 milliseconds, minimizing slippage and enhancing trading efficiency.
TMGM supports MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), available on PC, Mac, tablet, and mobile devices, accommodating diverse trading preferences. The broker provides educational resources, including a Trading Academy, live webinars, daily market analysis, trading guides, and a real-time economic calendar to keep traders informed. Clients also benefit from multilingual support, dedicated account managers, and efficient withdrawal processing for a seamless trading experience.
Free Forex Trading Courses and Resources
Achieving success in forex trading requires skill, knowledge, and practice. TMGM provides all the resources needed, including free forex trading courses and webinars. It also offers a free demo account funded with US$100,000 in virtual capital to build confidence in a risk-free environment.
Additionally, TMGM supplies trading strategy insights, market analysis, and educational articles for all skill levels—whether you' are a beginner or an experienced trader, TMGM has resources tailored for you. Register for an account today!