Trend Following

Le strategie di trading trend following mirano a trarre profitto dal movimento direzionale persistente dei prezzi degli asset. “Il trend è il tuo amico” è un detto spesso utilizzato in questo concetto fondamentale. I trader utilizzano strumenti come medie mobili e linee di tendenza per determinare se un mercato è in trend rialzista o ribassista. In un trend rialzista, i trader solitamente aprono posizioni long, mentre in un trend ribassista considerano posizioni short. Gli stop loss vengono posizionati al di sotto di livelli chiave di supporto per le operazioni long e al di sopra dei livelli di resistenza per le operazioni short. Per massimizzare i guadagni proteggendo i profitti, i trader spesso utilizzano stop loss trailing, che si adattano man mano che il prezzo si muove a loro favore.
Breakout Trading
Il breakout trading cattura forti movimenti di prezzo dopo una fase di consolidamento del mercato. I trader identificano livelli chiave di supporto e resistenza o pattern grafici per anticipare potenziali breakout e capitalizzare su periodi di volatilità aumentata. Gli ordini di acquisto vengono piazzati quando il prezzo rompe al di sopra della resistenza, mentre gli ordini di vendita vengono piazzati al di sotto del supporto. Gli ordini stop loss iniziali sono posizionati all’interno della zona di consolidamento per limitare il rischio. Gli obiettivi di profitto sono tipicamente fissati in base all’altezza del pattern' o ai livelli di swing precedenti per massimizzare i ritorni.
Strategie di Mean Reversion
La strategia di mean reversion si basa sull’assunto che i rendimenti storici e i prezzi stabiliti torneranno eventualmente alla loro media o “media” a lungo termine. I trader utilizzano indicatori di momentum come il Relative Strength Index (RSI) o le Bande di Bollinger per identificare condizioni di ipercomprato o ipervenduto. Vengono aperte posizioni controtrend quando gli indicatori mostrano divergenze, suggerendo una potenziale inversione. Poiché i trend a volte continuano inaspettatamente, i trader applicano stop loss stretti per minimizzare il rischio. Gli obiettivi di profitto sono generalmente fissati a livelli di prezzo medi storici o ai confini opposti delle Bande di Bollinger.
Trading basato su Notizie ed Eventi

Questa strategia è focalizzata sull’analisi fondamentale e si basa sulle reazioni del mercato a rilasci di dati economici, decisioni sui tassi di interesse o annunci sugli utili aziendali. I trader identificano eventi ad alto impatto e valutano i potenziali movimenti di mercato in base al fatto che i risultati effettivi siano in linea con le aspettative. Poiché tali eventi possono causare una volatilità elevata, alcuni trader utilizzano strategie basate su opzioni per gestire l’esposizione al rischio. È importante essere consapevoli di spread più ampi e liquidità ridotta intorno ai principali annunci, poiché le fluttuazioni di prezzo possono risultare imprevedibili.
Trading basato sull’Azione del Prezzo
I trader che utilizzano l’azione del prezzo si basano sui movimenti storici dei prezzi su un grafico per prendere decisioni di trading, concentrandosi sui dati grezzi del prezzo anziché su indicatori tecnici come le medie mobili. Questa tecnica prevede l’analisi delle formazioni a candela, dei livelli di supporto e resistenza e dei pattern grafici senza fare affidamento eccessivo sugli indicatori. L’attenzione è rivolta alla comprensione della psicologia di mercato e al comportamento di acquirenti e venditori.
Il trading basato sull’azione del prezzo può essere applicato su diversi timeframe e funziona bene se combinato con una corretta gestione del rischio.
Analisi Multi-Timeframe
Per migliorare la precisione, molti trader combinano l’azione del prezzo con l’Analisi Multi-Timeframe. Ciò significa utilizzare un timeframe superiore per determinare la direzione dominante del trend, un timeframe medio per pianificare gli ingressi e un timeframe inferiore per perfezionare l’esecuzione precisa. Quando i segnali si allineano su diversi timeframe, si riduce l’informazione contraddittoria e si rafforza la qualità dell’impostazione del trade.
Il trading basato sull’azione del prezzo funziona in molte condizioni di mercato e su diversi timeframe. È più efficace se abbinato a una chiara gestione del rischio, come livelli di stop loss definiti e dimensionamento ragionevole delle posizioni.
Strategia di Hedging
L’hedging viene utilizzato per ridurre il rischio di perdita su un asset aprendo una posizione che compensa un’altra. I trader effettuano hedging durante condizioni di mercato incerte o prima di importanti annunci di notizie. L’hedging agisce come una polizza assicurativa per i tuoi investimenti e tipicamente coinvolge l’uso di derivati, come opzioni e contratti futures. Tuttavia, l’hedging riduce anche i potenziali guadagni e non è una strategia per massimizzare i profitti.
Strategia di Scalping
Questa strategia prevede l’esecuzione di numerose operazioni di piccola entità durante la giornata con l’obiettivo di trarre profitto da minime variazioni di prezzo, spesso nell’arco di secondi o minuti. Richiede esecuzione rapida, spread ridotti e disciplina rigorosa. Gli scalper cercano di accumulare un alto volume di piccoli guadagni, basandosi sulla convinzione che i micro-movimenti di prezzo siano più frequenti e più facili da catturare rispetto a quelli di grande entità.
Lo scalping è adatto a trader che preferiscono un trading attivo e veloce, ma potrebbe non essere ideale per i principianti a causa della sua intensità e rapidità.
Strategia di Day Trading
Il day trading è una strategia ad alto rischio e alto rendimento che prevede l’acquisto e la vendita di titoli all’interno della stessa giornata per trarre profitto da piccole fluttuazioni di prezzo ed evitare i rischi overnight. Indicatori di momentum, pattern grafici a breve termine e calendari delle notizie di mercato sono strumenti utilizzati nel day trading.
Questa strategia richiede un monitoraggio frequente del mercato durante le sessioni di trading attive.
Strategia di Swing Trading
Lo swing trading mira a catturare movimenti di prezzo a breve-medio termine che durano da pochi giorni a diverse settimane. Funziona bene quando i mercati sono in trend regolare. Questa strategia offre flessibilità ed è adatta a trader part-time. Fornisce un equilibrio tra il ritmo rapido del day trading e il mantenimento a lungo termine tipico dell’investimento tradizionale.
Strategia di Position Trading
Il position trading si concentra sui trend di mercato a lungo termine. Mira a catturare movimenti di prezzo significativi su lunghi periodi, tipicamente settimane, mesi o addirittura anni. Pazienza, una prospettiva a lungo termine, ignorare il rumore della volatilità e focalizzarsi maggiormente sul sentiment di mercato sono elementi cruciali per questa strategia. Richiede ai trader di avere una visione chiara a lungo termine. I position trader utilizzano una combinazione di analisi fondamentale e tecnica per identificare i punti di ingresso e uscita corretti.
Consigli di Gestione del Rischio per il Trading CFD
Dimensionamento della Posizione
Un dimensionamento efficace della posizione è un aspetto fondamentale della gestione del rischio. Garantisce che nessuna singola operazione influenzi significativamente il capitale complessivo. Una regola comune è rischiare non più del 1–2% del capitale di trading su ogni operazione. Le dimensioni delle posizioni dovrebbero essere calcolate in base al posizionamento dello stop loss, assicurando che le perdite potenziali rimangano entro limiti accettabili.
Posizionamento dello Stop-Loss
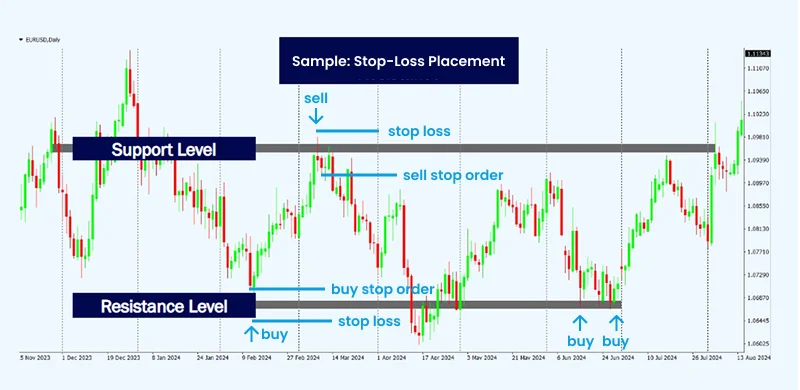
Il posizionamento strategico dello stop loss è fondamentale per proteggersi da perdite inutili. Invece di distanze di prezzo arbitrarie, gli stop dovrebbero essere fissati a livelli tecnici chiave, come zone di supporto o resistenza, per ridurre le probabilità di attivazioni premature. Considerare la volatilità di mercato nel determinare l’ampiezza dello stop aiuta a evitare di uscire da un trade troppo presto. Per una sicurezza aggiuntiva, i trader possono utilizzare ordini di stop loss garantiti, soprattutto durante eventi economici importanti, per limitare il rischio derivante da gap di prezzo improvvisi o movimenti estremi del mercato.
Rapporti Rischio-Rendimento
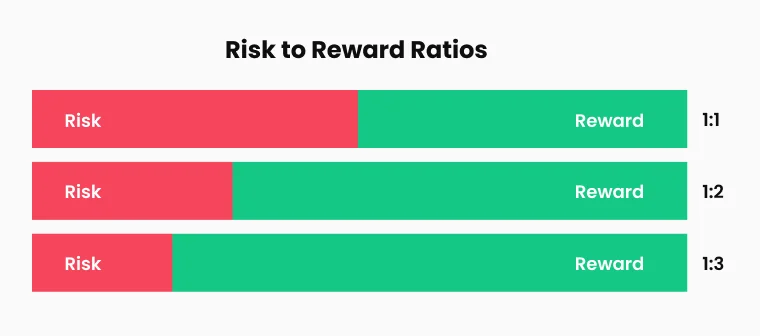
Il rapporto rischio-rendimento è fondamentale per la redditività a lungo termine. I trader spesso mirano a un rapporto minimo di 1:2, il che significa rischiare un’unità di capitale per guadagnarne potenzialmente due. Rapporti più elevati, come 1:3 o superiori, consentono ai trader di rimanere profittevoli anche con tassi di successo più bassi. Fissare obiettivi di profitto realistici basati sulle condizioni di mercato attuali aiuta a evitare di mantenere posizioni per guadagni irrealistici. Alcuni trader optano per chiusure parziali delle posizioni, assicurando profitti su una parte dell’operazione mentre lasciano correre il resto per movimenti di mercato più estesi.
Rischio di Correlazione
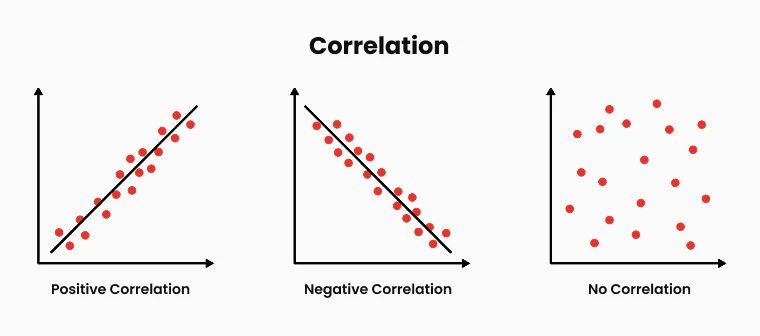
Gestire il rischio di correlazione è cruciale per evitare un’esposizione eccessiva a movimenti di mercato simili. Mantenere più posizioni in mercati altamente correlati può aumentare involontariamente il rischio, poiché i movimenti di prezzo in un asset possono influenzarne direttamente un altro. Comprendere le relazioni tra classi di asset, come coppie forex, materie prime e indici, aiuta i trader a diversificare l’esposizione. Monitorare l’esposizione delta complessiva del portafoglio assicura che i rischi direzionali rimangano bilanciati. L’utilizzo di matrici di correlazione può aiutare a identificare relazioni di mercato nascoste, prevenendo concentrazioni di rischio non intenzionali.
Consigli per il Trading CFD per Principianti
Il trading CFD comporta più della semplice selezione delle strategie giuste; richiede disciplina, consapevolezza del mercato e apprendimento continuo. Ecco alcuni consigli essenziali per migliorare le tue performance nel trading CFD:
Inizia con un Conto Demo: Esercitati nel trading CFD utilizzando prima un conto demo. Questo ti permette di familiarizzare con le piattaforme di trading, testare strategie e comprendere la dinamica del mercato senza rischiare capitale reale.
Mantieni la Disciplina nel Trading: Sviluppa un piano di trading scritto chiaramente che delinei punti di ingresso e uscita, dimensionamento delle posizioni e regole di gestione del rischio. Attieniti rigorosamente al tuo piano per evitare decisioni impulsive guidate dalle emozioni.
Usa Ordini Stop-Loss e Take-Profit: Imposta sempre livelli predefiniti di stop loss e take profit. Questi strumenti aiutano a gestire efficacemente il rischio limitando le perdite potenziali e assicurando i profitti quando le condizioni di mercato diventano favorevoli.
Rimani Informato e Aggiornato: Tieniti aggiornato con le notizie di mercato, indicatori economici ed eventi geopolitici che possono influenzare significativamente la volatilità del mercato. Utilizza calendari economici per anticipare eventi potenzialmente movimentati per il mercato.
Concentrati sui Rapporti Rischio-Rendimento: Punta a rapporti rischio-rendimento favorevoli (almeno 1:2 o superiori) per assicurarti che i potenziali guadagni superino significativamente le possibili perdite nel tempo. Questo approccio migliora la redditività anche con un tasso di successo moderato.
Tieni un Diario di Trading: Documenta le tue operazioni, annotando la motivazione dietro ogni decisione, le condizioni di mercato e i risultati. Rivedere regolarmente il diario di trading aiuta a identificare schemi di successo e aree di miglioramento.
Rivedi e Adatta Regolarmente le Strategie: I mercati evolvono e le strategie che hanno funzionato in passato potrebbero richiedere aggiustamenti. Valuta regolarmente le tue performance e adatta di conseguenza le strategie per rimanere efficace in condizioni di mercato mutevoli.
Integrando questi consigli pratici nella tua routine di trading CFD, potrai migliorare il tuo approccio al mercato, affinare il processo decisionale e raggiungere maggiore coerenza e successo nelle tue attività di trading.