POPULAR ARTICLES

- The US Dollar remains depressed near lows, weighed by Fed Powell's dovish turn.
- BoJ's Ueda has hinted at further interest rate hikes, providing additional support to the Yen.
- USD/JPY remains within previous ranges, yet with bearish momentum growing.
,
The US Dollar’s recovery attempts from Friday’s lows at 146.60 against the Japanese Yen have been capped around the mid-range of the 147.00s on Monday as the pair remains on the defensive amid an unfavourable monetary policy divergence following Fed Powell’s dovish comments.
Jerome Powell shocked markets with an unusually dovish tone in front of the world’s major central bankers at Jackson Hole, acknowledging the increasing downside risks for the US economy amid a deteriorating labour market.
Powell also said that the theory of a one-off inflationary impact from tariffs seems reasonable, and that the bank will be forced to adjust its monetary policy stance in a clear hint at interest rate cuts.
The BoJ Governor, Kazuho Ueda, on the other hand, struck a more hawkish tone in the same meeting. Ueda observed that the tighter labour market is pushing wages higher, paving the path for further monetary tightening in the coming months.
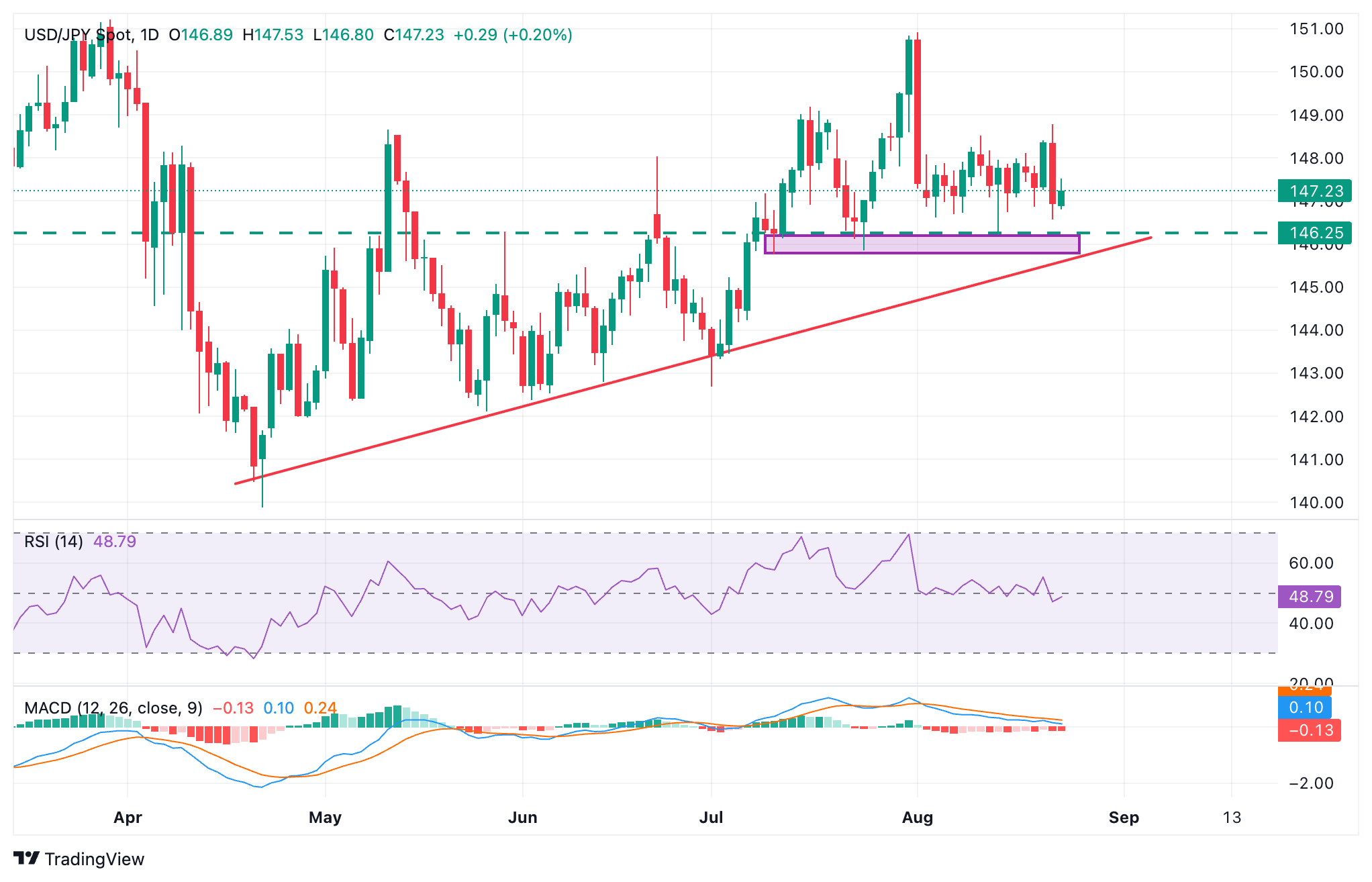
The Yen jumped about 1.34% against the US Dollar on Friday, posting an impulsive negative candle on the daily chart. Friday's strong reversal suggests the possibility of a deeper correction from late July highs, although the pair should breach supports at 146.25 and 1.4585 to confirm the bearish trend.
USD/JPY Daily Chart
Central banks FAQs
Central Banks have a key mandate which is making sure that there is price stability in a country or region. Economies are constantly facing inflation or deflation when prices for certain goods and services are fluctuating. Constant rising prices for the same goods means inflation, constant lowered prices for the same goods means deflation. It is the task of the central bank to keep the demand in line by tweaking its policy rate. For the biggest central banks like the US Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB) or the Bank of England (BoE), the mandate is to keep inflation close to 2%.
A central bank has one important tool at its disposal to get inflation higher or lower, and that is by tweaking its benchmark policy rate, commonly known as interest rate. On pre-communicated moments, the central bank will issue a statement with its policy rate and provide additional reasoning on why it is either remaining or changing (cutting or hiking) it. Local banks will adjust their savings and lending rates accordingly, which in turn will make it either harder or easier for people to earn on their savings or for companies to take out loans and make investments in their businesses. When the central bank hikes interest rates substantially, this is called monetary tightening. When it is cutting its benchmark rate, it is called monetary easing.
A central bank is often politically independent. Members of the central bank policy board are passing through a series of panels and hearings before being appointed to a policy board seat. Each member in that board often has a certain conviction on how the central bank should control inflation and the subsequent monetary policy. Members that want a very loose monetary policy, with low rates and cheap lending, to boost the economy substantially while being content to see inflation slightly above 2%, are called ‘doves’. Members that rather want to see higher rates to reward savings and want to keep a lit on inflation at all time are called ‘hawks’ and will not rest until inflation is at or just below 2%.
Normally, there is a chairman or president who leads each meeting, needs to create a consensus between the hawks or doves and has his or her final say when it would come down to a vote split to avoid a 50-50 tie on whether the current policy should be adjusted. The chairman will deliver speeches which often can be followed live, where the current monetary stance and outlook is being communicated. A central bank will try to push forward its monetary policy without triggering violent swings in rates, equities, or its currency. All members of the central bank will channel their stance toward the markets in advance of a policy meeting event. A few days before a policy meeting takes place until the new policy has been communicated, members are forbidden to talk publicly. This is called the blackout period.








