What Are Pattern Day Trading Rules?
Pattern day trading rules constitute a vital regulatory framework within the U.S. securities markets that every active trader should thoroughly understand to trade effectively and in compliance with the law.
Implemented by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) in 2001 following the dot-com bubble collapse, these rules aim to protect retail investors from the risks associated with frequent trading.
The pattern day trading rules specifically address individual investors who execute multiple day trades within short periods. They mandate maintaining higher minimum account equity and impose stricter trading restrictions.
Day Trading and Pattern Day Traders
A day trade occurs when a trader buys and sells (or sells short and subsequently covers) the same security within a single trading session.
An investor is designated a pattern day trader (PDT) under these rules if they execute four or more day trades within five consecutive business days, provided these trades constitute more than 6% of their total trading activity during that timeframe.
This classification triggers specific regulatory requirements and restrictions that substantially affect a trader’s market operations.'
Regulatory Purpose of PDT Rules
Understanding pattern day trading rules is not merely a compliance requirement— but a foundational element in developing a sustainable trading strategy within U.S. markets.
These regulations influence strategy formulation, capital allocation, risk management protocols, and the psychological discipline necessary for trading decisions.
For both novice and seasoned traders, a thorough understanding of these rules forms the basis for compliant and potentially profitable trading operations.
Historical Development of Pattern Day Trading Rules
The dot-com boom of the late 1990s led to a surge in retail day trading, driven by online trading platforms that lowered barriers to entry. Many inexperienced traders engaged in high-frequency trading without adequate risk controls.
Dot-Com Bubble & Regulatory Response
Retail investors incurred significant losses when the dot-com bubble burst (2000-2001). In response, FINRA (formerly NASD) and the SEC introduced pattern day trading rules to safeguard investors. These rules were proposed in 1999, opened for public consultation in 2000, and implemented in February 2001 amid the market downturn.
A New Regulatory Approach
Rather than banning day trading outright, regulators imposed elevated capital requirements to ensure traders possess adequate financial resources. This risk-based framework aims to balance investor protection with market access, although its effectiveness remains subject to debate.
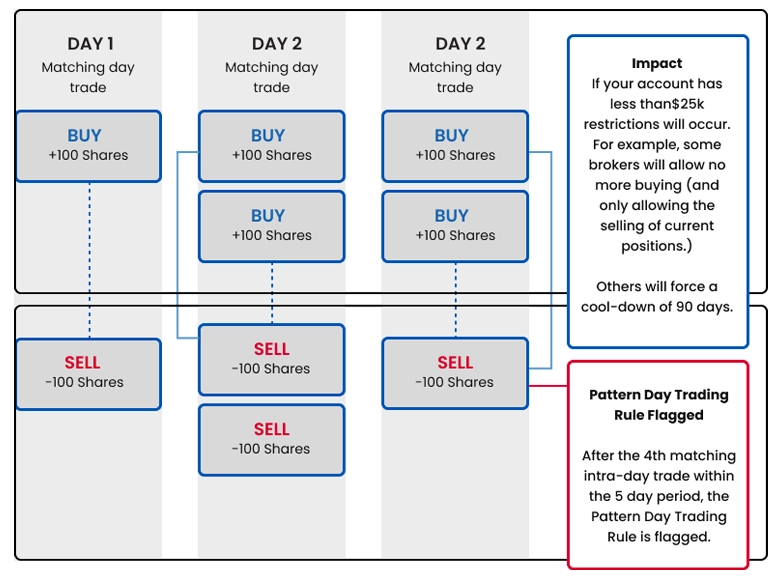
Figure 1: Pattern Day Trading: How is it Defined?
Core Components of the Pattern Day Trading Rules
Pattern day trading rules are based on several fundamental components that determine who is subject to these regulations and the requirements they must fulfill.
A clear understanding of these elements is crucial for any trader aiming to operate within regulatory compliance.
Classification Criteria and Thresholds
A trader is classified as a pattern day trader (PDT) if they execute four or more day trades within a rolling five-business-day period and these trades constitute over 6% of their total trading volume during that period.
PDT status applies to the individual trader, not merely a single account. If a trader holds multiple accounts with the same brokerage, their trading activity is typically aggregated for classification purposes.
Additionally, brokers may proactively designate a client as a pattern day trader if there is reasonable belief that the client will engage in frequent day trading.
Minimum Equity Requirement
Once classified as a pattern day trader, the primary obligation is to maintain a minimum equity balance in the trading account. According to FINRA, pattern day traders must maintain at least US$25,000 in equity within their margin accounts at all times.
This equity can comprise cash and eligible securities. If the account equity falls below US$25,000, the trader is prohibited from executing day trades until the minimum equity threshold is restored. The US$25,000 minimum must be met prior to engaging in any day trading activity.
Regulatory Rationale Behind Capital Requirements
This substantial capital requirement serves several regulatory objectives within the pattern day trading framework:
It ensures traders have significant financial resources at risk, promoting more prudent trading decisions;
It provides a buffer against rapid losses associated with frequent trading; and
It restricts day trading activity to traders with adequate financial capacity, effectively filtering out undercapitalized investors.
Enhanced Day Trading Buying Power
Pattern day traders receive certain privileges alongside their increased obligations. A key benefit is enhanced intraday buying power, often referred to as "day trading buying power."
Pattern day traders meeting the minimum equity requirement typically have 4:1 intraday buying power, meaning they can open positions up to four times their maintenance margin excess.
This enhanced buying power applies exclusively to intraday positions; overnight holdings remain subject to standard margin requirements (generally 2:1).

Figure 2: Pattern Day Trader Rule for Margin Accounts under US$25,000
Margin Call Mechanisms
If a pattern day trader exceeds their buying power, brokers issue a day trading margin call, requiring additional funds within five business days. Failure to meet this call restricts the account to cash-only trading for 90 days or until the margin call is satisfied.
Consequences of Violating PDT Rules
Violations of pattern day trading rules trigger automatic trading restrictions that limit account activity until compliance is restored.
Immediate Account Restrictions
If a trader fails to maintain the US$25,000 minimum equity or exceeds the three-day-trade limit, their account is flagged for violations. Day trading privileges are suspended, and trading is restricted to cash-only transactions until the account returns to compliance.
Day Trading Margin Call Process
Exceeding day trading buying power results in a margin call, requiring additional funds within five business days. Until resolved, trading capacity is limited. If the call remains unmet, the account is restricted to cash-only trading for 90 days.
Escalating Penalties for Repeated Violations
Repeated violations may lead to forced liquidation of positions, account suspensions, or termination of brokerage services. Persistent non-compliance could be reported to FINRA, potentially affecting future account approvals.

Strategies for Operating Within Pattern Day Trading Rules
Traders unable to meet the US$25,000 minimum equity requirement must adopt specific strategies to remain active in the markets while avoiding classification as pattern day traders.
Several approaches have become common practice for operating within these regulatory constraints.
Alternative Trading Styles
For traders below the PDT threshold, alternative trading styles enable active market participation without triggering pattern day trading rules:
Swing trading: Holding positions overnight or for multiple days allows active trading without day trade classification
Position trading: Taking longer-term positions based on fundamental analysis avoids frequent trading concerns
Options strategies: Utilizing defined-risk options spreads held for several days offers leveraged exposure with limited capital
Sector rotation: Concentrating on broader market trends rather than rapid entry and exit timing
These strategies allow traders to develop their skills and grow their accounts toward the PDT threshold while remaining compliant with regulations.
Strategic Day Trade Management
Traders aiming to avoid PDT classification must monitor their day trades within the rolling five-day window and manage trade frequency carefully.
Reserving day trades for high-conviction setups with favorable risk-reward profiles ensures efficient use of limited day trades. Some traders adopt a strategy of one day trade per week for sustainability.
Utilizing paper trading platforms allows strategy testing without consuming actual day trades, enabling skill refinement risk-free.
This disciplined approach enables traders to capitalize on occasional day trades while avoiding PDT restrictions.
Multiple Brokerage Approach
Some traders distribute their trading activity across multiple brokerages to increase their effective day trade capacity. Opening accounts at several brokers allows up to three day trades per five business days at each institution.
Different account types within the same brokerage may be treated separately for PDT purposes. Diversifying across brokers also provides redundancy in case of technical issues on a particular platform.
While this method can expand day trading capacity, it requires meticulous record-keeping and account coordination. Traders should also be aware that deliberately structuring accounts to circumvent regulatory requirements could violate FINRA rules, although enforcement against small retail traders is uncommon.

Figure 3: Margin Account vs. Cash Account
Pattern Day Trading Rules and Different Account Types
The application of pattern day trading rules varies significantly depending on the brokerage account type, creating critical distinctions traders must understand.
Cash vs. Margin Account Distinctions
Cash accounts are exempt from PDT rules but must comply with T+2 settlement for equities. They cannot trade using unsettled funds, as this results in good faith violations. While no specific day trading limits apply, all trades must be funded with settled cash, and no minimum equity requirement exists.
Margin Account Implications
Margin accounts are fully subject to PDT rules and are classified as PDT after four day trades within five business days. Once classified, a US$25,000 minimum equity is required, but traders benefit from enhanced buying power and exemption from settlement delays. Some traders use cash accounts to avoid PDT restrictions while building capital.
Retirement Account Considerations
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), including Traditional and Roth, typically prohibit margin trading, exempting them from PDT rules. However, they remain subject to settlement requirements similar to cash accounts. Some brokerages impose additional trading restrictions, and frequent trading in retirement accounts may have adverse tax consequences, making them less suitable for active trading.
Professional and Institutional Accounts
Certain account categories operate under modified PDT rules. Professional traders may be subject to different classification criteria, while market makers and proprietary trading firms often receive exemptions. Institutional accounts follow separate regulatory frameworks tailored to their capital and expertise, distinct from retail PDT regulations.
The Pattern Day Trading Rules in Today’s Market
Evolving Market Conditions
Since the implementation of pattern day trading (PDT) rules in 2001, financial markets have evolved considerably, prompting questions about their current relevance.
Technological Advancements
Retail traders now benefit from commission-free trading, sophisticated charting tools, mobile platforms, algorithmic trading capabilities, and social media-driven insights, enhancing accessibility and accelerating trading frequency—potentially conflicting with regulations designed for earlier market conditions.
Market Structure Shifts
High-frequency trading dominates volume, liquidity is fragmented across dark pools, ETFs drive significant trading activity, and extended trading hours create new opportunities. These developments challenge the effectiveness of PDT rules originally designed for traditional market structures.
Calls for Regulatory Updates
Market participants have proposed adjusting the US$25,000 minimum for inflation, implementing tiered capital requirements based on risk profiles, offering educational alternatives to capital thresholds, and harmonizing rules across account types. However, FINRA and the SEC continue to prioritize capital-based investor protection.
Global Regulatory Perspectives
Unlike the U.S., Europe’s MiFID II framework emphasizes transparency rather than PDT-style restrictions. Asian markets vary: Japan enforces stringent margin controls, while Hong Kong and Singapore focus on preventing market manipulation rather than limiting trade frequency.
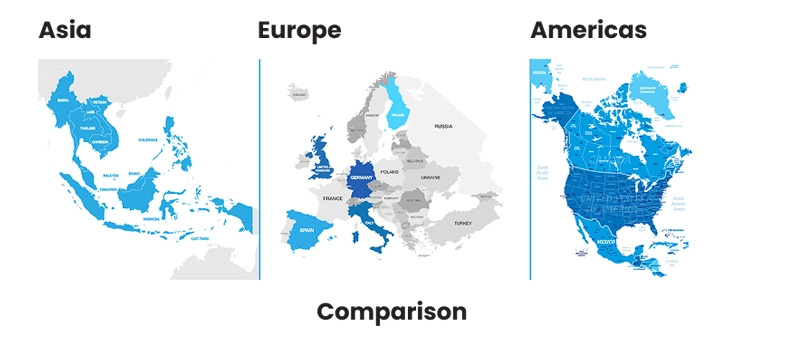
Figure 4: Comparison between Asia, Europe and America
Regulatory Arbitrage Considerations
International disparities in day trading regulations enable traders to circumvent U.S. PDT rules by utilizing offshore brokers or foreign markets with fewer restrictions—with some brokers even promoting PDT rule avoidance as a service.
This raises concerns about the global competitiveness of U.S. markets and whether PDT rules drive retail traders to less regulated jurisdictions, potentially undermining market oversight.
Practical Compliance Strategies: Navigating Pattern Day Trading Rules Effectively
Building Toward PDT Compliance
Traders targeting the US$25,000 equity threshold can employ structured approaches such as regular capital injections, conservative trading to preserve capital, and a balanced portfolio combining active trading with longer-term investments. Tracking progress with milestones and exploring legal structures may expedite compliance.
Effective Record-Keeping
Maintaining comprehensive trade logs, equity statements, margin call notifications, and broker correspondence ensures regulatory compliance and protects against disputes. Proper documentation helps prevent inadvertent PDT violations.
Broker Selection & and Management
Brokerages differ in PDT rule enforcement, availability of one-time flag removals, and automated trade tracking tools. Platforms with intuitive interfaces displaying day trade usage and responsive customer support facilitate compliance management.
Education & and Professional Development
Traders can leverage PDT constraints to enhance their skills through educational programs, market simulations, mentorship, and professional certifications. This preparation strengthens long-term trading success once PDT restrictions are lifted.

Impact of Pattern Day Trading Rules on Market Dynamics
Pattern day trading rules influence individual trader behavior and broader market dynamics in subtle yet significant ways.
Retail Participation Patterns
PDT rules shape retail trading behavior by encouraging traders to hold overnight or multi-day positions rather than engaging in intraday trades. Consequently, retail activity tends to concentrate around market open and close, while high-net-worth traders maintain unrestricted access. This stratification affects market liquidity, price discovery, and volatility, particularly in stocks with strong retail interest.
Impact on Market Liquidity
PDT rules may reduce liquidity in small-cap stocks, as retail traders trade less frequently. Well-capitalized traders dominate liquidity provision, compelling market makers to adjust strategies. Midday trading volumes often decline due to retail trading restrictions, potentially impacting overall market efficiency.
Influence on Volatility and Price Action
Restricted retail trading affects volatility patterns, especially in stocks favored by retail traders. Volatility spikes at market open and close occur as traders concentrate limited day trades during these periods. Overnight price gaps become more pronounced since PDT rules compel traders to hold positions beyond trading hours. These effects illustrate how regulations influence market behavior beyond their intended investor protection objectives.

Future of Pattern Day Trading Rules
Despite evolving markets and technological advancements, pattern day trading rules have remained largely unchanged for over twenty years. As retail participation expands, these rules face increasing scrutiny regarding their effectiveness. Potential future modifications may include raising minimum equity thresholds, introducing educational alternatives, leveraging technology for risk management, and aligning regulations globally to reduce arbitrage. Until such changes occur, traders must operate strategically within existing constraints, emphasizing discipline and risk management to succeed.
Unlock Your Trading Potential with TMGM
At TMGM, we equip traders with the tools, expertise, and market access necessary to navigate the complexities of pattern day trading rules. Whether optimizing your trading strategy, utilizing institutional-grade technology, or exploring global markets, TMGM offers the support and flexibility you need.
Trade smarter with advanced risk management, competitive trading conditions, and expert market insights. Join TMGM today and take control of your trading journey.