CFD Trading in India: What It is and How It Works
If you are exploring new ways to trade, understanding what is CFD trading can give you an edge over other traders worldwide. A CFD, or Contract for Difference, is a sophisticated financial instrument that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of underlying assets without owning them. In simple terms, the CFD meaning is that you and your broker agree to exchange the difference in as asset’s price between the time you open and close the trade. With CFD trading globally, traders can take advantage of both rising and falling markets while assessing a wide variety of asset classes such as: - Gold - Stock Indices - Forex - ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) - Cryptocurrencies CFD online trading is a popular choice for looking for these opportunities as everything can be managed on a single online platform, such as TMGM. By learning what is CFD and how it works, traders can diversify their strategies and benefit from the unique advantages CFDs offer compared traditional investing.
Key Features of CFD Trading
Leverage and Margin Trading
One of the biggest advantages of CFD trading globally is the use of leverage. When you trade CFD online, leverage allows you to control larger market positions while only using a fraction of the total capital as margin. This makes trading CFDs highly capital-efficient compared to traditional investing.
How Leverage Works in CFD Trading
Enhanced Market Exposure: With leverage, you can gain exposure to stocks, forex pairs, or commodities by depositing only a small margin.
Capital Efficiency: Instead of tying up all your funds in one trade, you can use CFDs to diversify across multiple markets with the same capital.
Amplified Potential: Profits and losses are calculated on the full position size, not just the margin you put down, which increases both risk and reward.
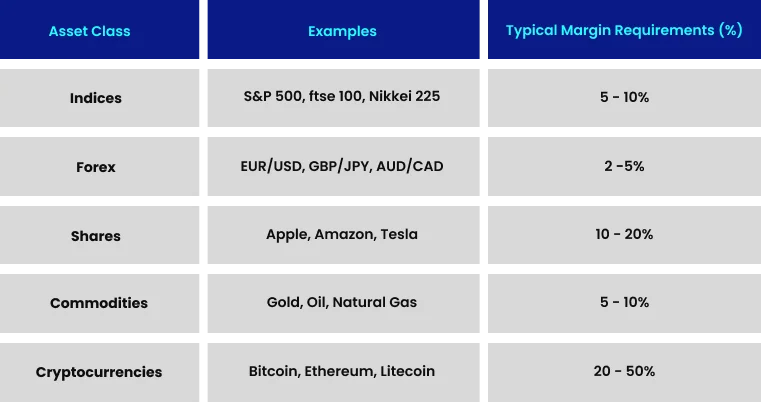
For example, with a 5% margin requirement on the S&P 500 index, a $1,000 deposit could expose you to a $20,000 position. A like-for-like example would be trading the Nifty 50 index or crude oil with a 5% margin requirement. With just ₹80,000 as margin, you could open a position worth ₹16,00,000. However, this amplification works both ways—magnifying potential profits and losses.
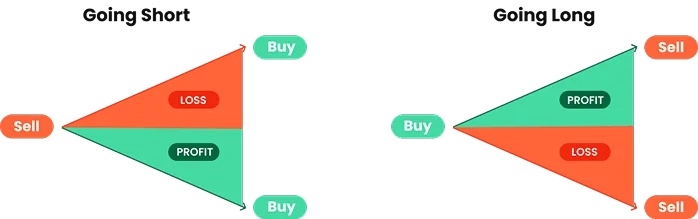
Going Long or Going Short
Unlike traditional investing in India where profits mostly come from buying and holding, CFDs give traders the ability to take advantage of both rising and falling prices:
Long Positions (Buy): If you expect an asset to rise, you can open a buy position.
Short Positions (Sell): If you believe prices will fall, you can open a sell position and profit from downward movements.
This two-way trading feature makes CFDs particularly valuable during times of market volatility or economic uncertainty. By understanding the meaning of CFD, and how leverage and margin function, traders can better navigate opportunities across equities, forex, commodities, and global indices.
Diverse Market Access
CFD trading provides access to thousands of financial markets through a single platform:
With over 18,000 markets available, traders can diversify their portfolios and capitalize on opportunities across different sectors and regions.
How CFD Trading Works: A Practical Breakdown
Position Sizing and Contract Values
CFD positions are measured in contracts or lots, with each market having its specific contract value:
Shares CFDs: Typically, one contract equals one share
Index CFDs: Contract values usually expressed as a currency amount per index point (e.g., $10 per point)
Forex CFDs: Standardized lot sizes (standard lot = 100,000 units of base currency)
Understanding the contract value is essential for calculating potential profits, losses, and position sizing based on your risk tolerance.
The Mechanics of Profit and Loss
CFD profit and loss calculations follow a straightforward formula:
For long positions (buy): Profit/Loss = (Closing Price - Opening Price) × Number of Contracts × Contract Value
For short positions (sell): Profit/Loss = (Opening Price - Closing Price) × Number of Contracts × Contract Value
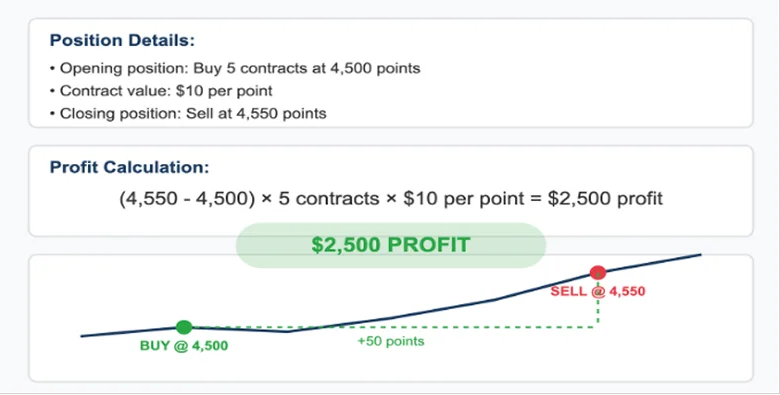
Example: Long Position on S&P 500 Index
Opening position: Buy 5 contracts at 4,500 (contract value: $10 per point)
Closing position: Sell at 4,550
Calculation: (4,550 - 4,500) × 5 × $10 = $2,500 profit
Example: Short Position on S&P 500 Index
Opening position: Sell 5 contracts at 4,500 (contract value: $10 per point)
Closing position: Buy at 4,450
Calculation: (4,500 - 4,450) × 5 × $10 = $2,500 profit
It is important to note that these examples exclude costs and charges such as overnight funding, spreads, or commissions.
Understanding the Spread in CFD Trading
When learning CFD trading in the global market, one of the most important concepts to grasp is the spread. In simple terms, the CFD meaning of a spread is the difference between the buy (ask) price and the sell (bid) price quoted by your broker. This cost is built into every trade you make in CFD online markets.
For most markets such as indices, forex pairs, and commodities, the primary cost of CFD trading is included in the spread itself.
For share CFDs, some brokers may charge a small commission instead of widening the spread.
Tighter spreads are always more beneficial because they reduce the amount of market movement needed for your trade to become profitable.
For Indian traders exploring CFD, understanding spreads is critical. For example, when trading gold CFDs, a tighter spread means you can enter and exit positions more efficiently, saving on trading costs. By paying attention to spreads, traders in India can improve their overall strategy and make better use of the flexibility that CFD trading provides.
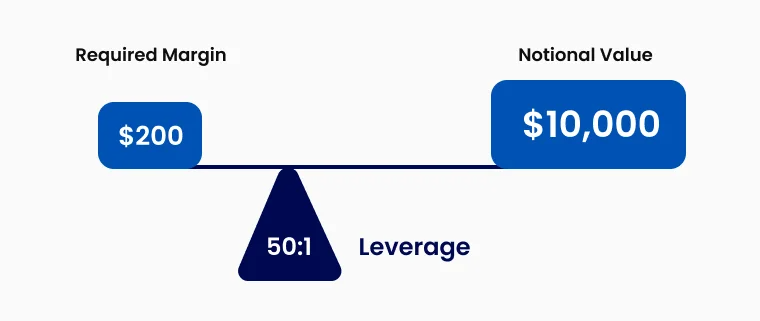
Margin and Leverage Calculations
To calculate the margin required for a position:
Margin Requirement = Position Size × Margin Percentage
For example, to open a position worth $10,000 on the market with a 10% margin requirement:
$10,000 × 10% = $1,000 initial margin required.
Effective leverage is calculated as: Effective Leverage = Position Size ÷ Margin Requirement.
In the example above, the effective leverage would be 10:1 ($10,000 ÷ $1,000).
Advanced CFD Trading Concepts
Hedging with CFDs
For traders in India, one of the most practical uses of CFD trading is hedging. By understanding the CFD meaning, investors can use these instruments to protect their existing portfolios from market volatility while still staying invested.
Portfolio Protection: If you hold a traditional share portfolio valued at $50,000 (the equivalent of around ₹40 lakh), you could open a short CFD position of equivalent value. If the market falls, the profit on your CFD position can offset losses in your share portfolio.
Sector Hedging: Protect against sector-specific risks by taking opposing positions in related markets.
Currency Risk Management: Hedge against currency exposure in international investments.
This flexibility makes CFDs an effective risk management tool, especially in times of high volatility or economic uncertainty.
Rolling Contracts vs. Futures CFDs
CFD providers generally offer two types of contracts: Cash (Rolling) CFDs and Futures CFDs, each with distinct characteristics suited to different trading strategies.
Cash or Rolling CFDs
Rolling CFDs do not have a fixed expiry date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. However, they are subject to overnight funding charges, which can accumulate over time. This makes them ideal for short to medium-term trading, where traders seek to capitalize on price movements without concerns about contract expiration.
Futures CFDs
Futures CFDs come with a fixed expiry date, meaning they automatically close at a predetermined time. Unlike rolling CFDs, no overnight funding charges apply, as all costs are already built into the spread. This structure makes futures CFDs more suitable for medium to long-term positions, where traders aim to avoid daily financing costs.
Choosing between rolling and futures CFDs depends on your trading timeframe and strategy. Short-term traders may prefer rolling CFDs for flexibility, while those holding longer-term positions may benefit from the cost structure of futures CFDs.
Order Types and Risk Management
Successful CFD trading relies on effective order execution and risk management tools:
Market Orders: Execute immediately at the current market price
Limit Orders: Set a specific price for entry
Stop Orders: Automatically open positions when markets reach specified prices
Stop-Loss Orders: Close positions to limit losses
Take-Profit Orders: Secure profits at predetermined price levels
Guaranteed Stops: Ensure execution at exact price levels (usually for an additional premium)
Trailing Stops: Dynamic stop-loss orders that move with favorable market movements
A comprehensive risk management strategy incorporating these tools is essential for sustainable trading.
Is CFD Trading Right for You?
Advantages of CFD Trading
Market Versatility: Trade multiple asset classes from a single platform
Leverage Benefits: Control larger positions with smaller capital outlay
Shorting Capability: Profit from falling markets without borrowing securities
No Stamp Duty: In some jurisdictions, CFDs are exempt from stamp duty that applies to share purchases
Extended Market Hours: Access to out-of-hours trading on major indices
Hedging Potential: Protect existing investments against market downturns
Risks and Considerations
Magnified Losses: Leverage can amplify losses, potentially exceeding your initial deposit
Overnight Funding Costs: Long-term positions incur daily financing charges
Market Volatility: Rapid price movements can trigger stop-loss orders or margin calls
Counterparty Risk: Reliance on the CFD provider’s financial stability
Complexity: Requires understanding of multiple financial concepts and markets
Why You Should Trade CFDs?
Understanding CFD trading is an important step in deciding whether it suits you as an investor. CFD trading is best suited for individuals globally who have a strong knowledge of financial markets and can dedicate time to analysing price movements, monitoring positions, and applying disciplined strategies.
Successful traders in CFD online markets often rely on strict risk management practices to minimize potential losses and maximise returns. Since CFDs are leveraged products, having sufficient financial resources is critical. Traders must be able to withstand price fluctuations without being forced to exit positions too early.
A clear grasp on CFD, and how leverage magnifies both gains and losses is essential for effective risk management. Traders around the globe who can combine this knowledge with a structured trading approach may find CFD trading to be a practical and flexible way to participate in global and domestic markets.
5 Steps to Becoming a Successful CFD Trader in India
For traders around the world who want to understand what is CFD trading and how to succeed in it, the journey requires preparation, discipline, and a structured approach. By learning the CFD trading meaning, practicing with CFD online trading tools, and applying risk management principles, you can steadily build the foundation for long-term success.
1. Build a Strong Knowledge Foundation
Before placing your first trade, make sure you have a solid grasp of what is CFD, how CFD pricing works, and the risks involved with leverage. Study both technical and fundamental analysis, risk management principles, and trading psychology. Many brokers offering CFD trading provide free resources such as webinars, tutorials, articles, and demo to accounts to help you gain the knowledge needed to trade with confidence.
2. Develop a Comprehensive Trading Plan
A structured trading plan is essential for consistency. Your plan should define:
Entry adn exit criteria
Position sizing rules
Risk parameters such as maximum daily or monthly losses
Timeframes and markets you will focus on
By documenting and sticking to your plan, depending on the market conditions, you can approach CFD online trading with discipline and long-term perspective.
3. Practice on a Demo Account
Before committing real capital, test your strategies on a demo account. This risk-free environment lets you experience live market conditions, understand how spreads and leverages impact trades, and refine your strategy without financial pressures. TMGM offers a free demo in India with virtual funds and real-time market data.
4. Start Small and Scale Gradually
When moving to live trading, begin with smaller position sizes and conservative leverage. Focus one one or two markets, such as gold or forex CFDs, before expanding. Scale up only after achieving consisten results, as this helps bridge the psychological gap between demo trading and live markets.
5. Continuously Review and Improve
Ongoing improvement is vital in CFD trading. Maintain a trading journal, track performance metrics, and analyze patterns in both winning and losing trades. Adapt your strategies to changing market conditions and stay updated with global and Indian market news. By consistently reviewing your process, you strengthen your ability to succeed CFD online markets.
Understanding CFD Costs and Fees
When exploring CFD trading, traders need to understand the costs involved, since these direct impact profitability. Knowing the CFD meaning is not good enough. Costs like spreads, commissions and overnight funding in CFD trading must be understood. By learning how these costs work in CFD online platforms, traders can better manage risk and plan their strategies effectively.
Spreads
The spread is the difference between the asset’s buy (ask) and sell (bid) price. It is the main cost when trading indices, forex pairs or gold with CFDs. Spreads can vary depending on mark conditions and volatility. For example, during major economic events or periods with low liquidity, spreads may widen, making trades more expensive to execute. Tight spreads are generally better because they reduce the market movement needed to break even.
Commissions
When trading share CFDs, brokers charge a commission instead of relying solely on spreads. This fee is usually a percentage of the trade value, and brokers may apply a minimum charge to ensure small trades cover their costs. For the traders on the global market, understanding these commission structures is crucial when selecting a broker for CFD online trading.
Overnight Funding
If you hold a CFD trading position past the daily cut-off time, you may incur an overnight funding fee (also called a swap rate). This charge depends on interbank lending rates plus the broker’s markup. Typically, long positions attract a charge, while short positions may sometimes earn a credit, depending on interest rate differences between currencies or assets. For traders dealing with forex CFDs, this can be a significant factor.
Guaranteed Stop-Loss Premiums
A guaranteed stop-loss order ensures that your trade closes at the exact level you specify, even if the market gaps beyond it. This extra layer of risk protection comes with a small premium, which is refunded if the stop-loss is not triggered. This features can be an effective way to manage risk when navigating volatile CFD online markets.
By understanding these costs in CFD trading, Indian traders can make informed decisions, optimize their strategies, and manage expenses more efficiently across global and domestic markets.
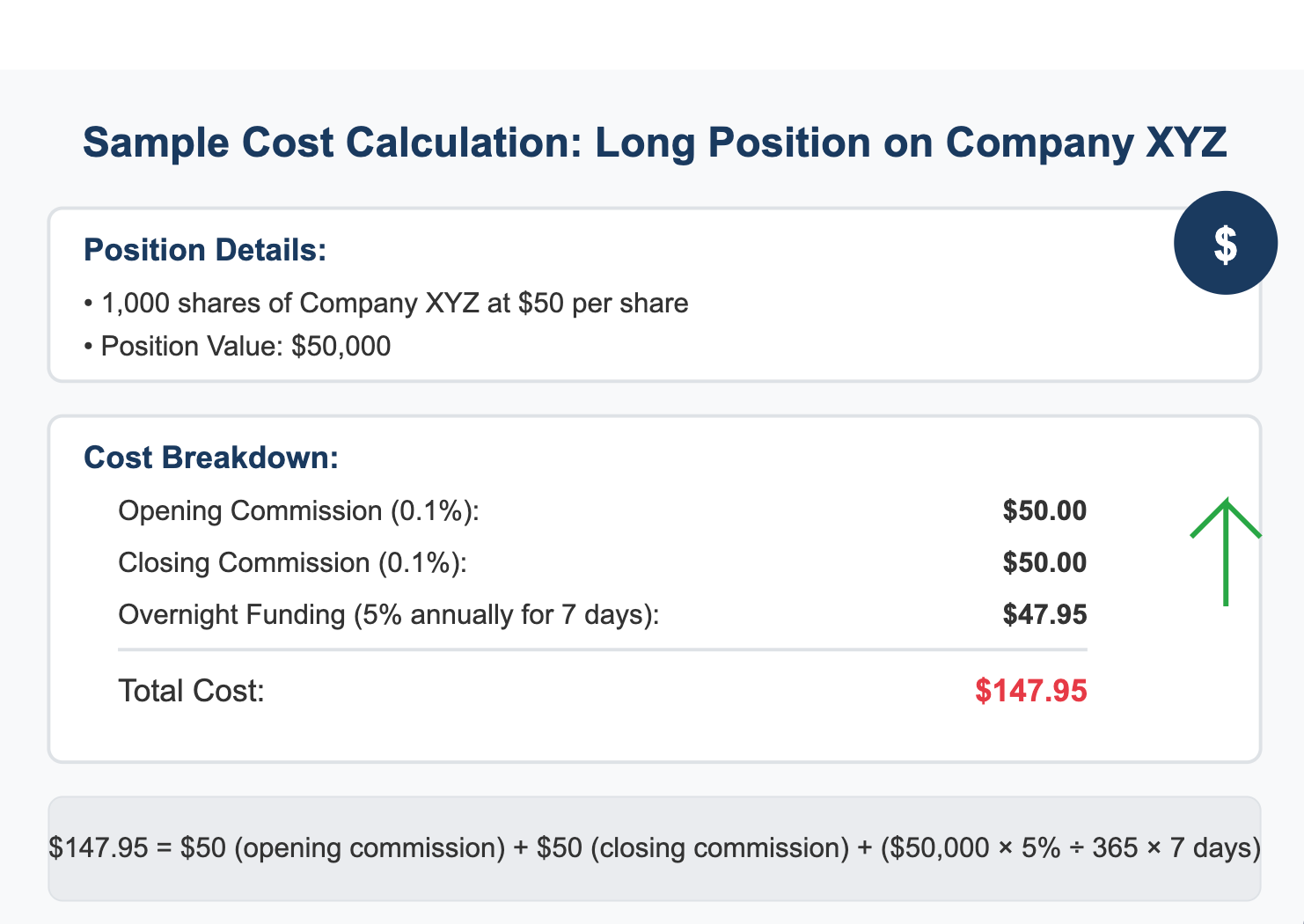
Sample Cost Calculation
For a long position on 1,000 shares of Company XYZ at $50 per share with a 0.1% commission:
Position value: $50,000
Opening commission: $50 (0.1% of $50,000)
Closing commission: $50 (assuming same price)
Overnight funding at 5% annually: Approximately $6.85 per day ($50,000 5% ÷ 365)
The total cost of holding the position for 7 days would be approximately $147.95 ($50 + $6.85 x 7).
Trading with TMGM
TMGM is the global leader in CFD trading, offering tight spreads starting from 0.0 pips on major currency pairs with competitive commission rates. Traders can access leverage up to 1:1000, benefiting from deep liquidity sourced from multiple tier-1 providers for efficient trade execution. The platform provides fast execution speeds, averaging under 30 milliseconds, minimizing slippage and improving trading efficiency.
TMGM supports both MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), available on desktop, web, and mobile devices, catering to various trading preferences. TMGM also provides educational resources, including a Trading Academy, live webinars, daily market analysis, trading guides, and a real-time trading calendar to keep traders informed. Clients also receive multilingual support, dedicated account managers, and efficient withdrawal processing, ensuring a seamless trading experience globally.
Free CFD Trading Course and Resources
Achieving success in CFD trading takes skill, knowledge, and practice. TMGM offers everything you need to get there, with a wealth of free trading courses and webinars to go deeper into the CFD meaning. It also offers a free demo account with $100,000 in virtual funds to help build your confidence in a risk-free environment.
We also provide trading strategy insights, market analysis, and news articles for all experience levels. Whether you’re a complete newcomer and want to understand CFD, or a seasoned trader, TMGM has something for you.
Trade Smarter Today




FAQs on CFD Trading
What is CFD trading and how does it work in India?
Is CFD trading legal in India?
What costs are involved in CFD trading for Indian traders?
Can I start CFD trading with small capital in India?

Account
Account
Instantly