Key Takeaways
Cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital asset based on blockchain technology, enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions.
Crypto trading can be conducted via CFDs, also known as Crypto CFD Trading , or through centralized exchanges, each offering distinct benefits.
Key concepts include leverage, margin trading, lot sizes, pips, and spreads.
Effective risk management is essential in crypto trading due to market volatility.
The Birth of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency originated with the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, following the global financial crisis. In October 2008, an anonymous individual or group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," which introduced the concept of a decentralized digital currency operating without intermediaries such as banks.
The first Bitcoin block, known as the "genesis block," was mined on January 3, 2009, marking the official launch of the world's first cryptocurrency. Initially, Bitcoin was primarily used by technology enthusiasts and privacy advocates. A notable transaction in 2010 involved purchasing two pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoin (now worth billions at current prices).
Following Bitcoin's introduction, other cryptocurrencies emerged:

Figure 1: Examples of other cryptocurrencies
Litecoin (2011) – Developed as a "lighter" alternative to Bitcoin with faster transaction processing times
Ripple (2012) – Designed for institutional payment networks
Ethereum (2015)– Introduced smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps)
Thousands of other cryptocurrencies have since been developed, each with unique features and use cases
Key Characteristics of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are digital assets designed to serve as a medium of exchange without reliance on centralized authorities such as governments or banks. They operate on decentralized networks and are secured through advanced cryptographic methods, ensuring security and resistance to counterfeiting. Unlike traditional fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies exist solely in digital form with no physical representation.
Many cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, have a capped supply with predefined maximum issuance limits (e.g., Bitcoin’’s cap of 21 million coins), which contributes to scarcity and value appreciation over time.
What is Cryptocurrency Trading?
Cryptocurrency trading involves speculating on price movements of cryptocurrencies either through a CFD trading account or by buying and selling the underlying tokens on an exchange. This allows traders to leverage the inherent volatility of crypto markets to potentially generate profits.
Traders employ various strategies depending on their objectives and risk tolerance. Day trading focuses on short-term price fluctuations, with positions opened and closed within the same trading day. Swing trading involves holding positions over several days or weeks to capitalize on broader price trends. Meanwhile, spot trading refers to buying and selling cryptocurrencies at current market prices for direct ownership without leverage. Each method carries distinct risks and benefits, and the choice depends on the trader’’s style and market outlook.
Two Main Ways to Trade Crypto
#1 Trade Crypto CFDs with TMGM
Crypto CFDs (Contracts for Difference) are derivative instruments that allow you to speculate on cryptocurrency price movements without owning the underlying tokens. With TMGM'’s crypto CFDs:
You can go long ('buy') if you anticipate the cryptocurrency’s value will increase
You can go short ('sell') if you expect the cryptocurrency’s value to decline
Both options utilize leverage, meaning you only need to deposit a fraction—known as margin—to gain full exposure to the underlying market.
Your profit or loss is calculated based on the total size of your position.
Leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses.
#2 Buying and Selling Cryptocurrencies via Centralized Exchanges
When purchasing cryptocurrencies through an exchange:
You acquire the actual cryptocurrency tokens
You must create and verify an exchange account
You need to deposit the full value of the asset to open a position
You are responsible for securely storing the cryptocurrency in your wallet until you' decide to sell
Trading via exchanges involves challenges:
A steep learning curve to understand blockchain technology
Complexity in interpreting market data
Deposit limits imposed by many platforms
Potentially high account maintenance fees
Security risks related to wallet management
How Do Cryptocurrency Markets Work?
Cryptocurrency markets operate fundamentally differently from traditional financial markets:
Decentralized Network Structure
Cryptocurrency markets are decentralized, meaning they are not issued or backed by any central authority such as a government. Instead, they operate across a distributed network of computers. Despite decentralization, cryptocurrencies can be bought and sold on exchanges and stored in 'digital wallets.'
Digital Asset Ownership Records
Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies exist solely as a shared digital ledger of ownership recorded on a blockchain. When a user sends cryptocurrency to another, the transfer is made to the recipient’s digital wallet. The transaction is not finalized until it is verified and appended to the blockchain through mining. This process also typically generates new cryptocurrency tokens.
What is Blockchain Technology?
A blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records data. For cryptocurrencies, it tracks the transaction history of every unit, showing how ownership has changed over time. Blockchain operates by recording transactions in 'blocks' which are sequentially added to the front of the chain.
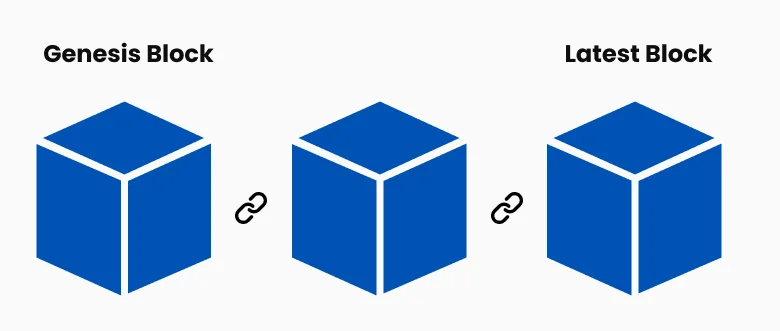
Figure 2: Blockchain Illustration
Advanced Security Features of Crypto and BlockchainUnique Security Features
Blockchain technology incorporates security features absent in standard computer files:
Consensus Mechanisms in Crypto Networks
A blockchain ledger is stored redundantly across numerous computers in the network – rather than a single centralized location – and is typically accessible to all network participants. This ensures transparency and makes it extremely difficult to alter data, eliminating single points of failure vulnerable to hacking or errors.
Cryptographic Foundations of Crypto
Blocks are cryptographically linked – employing advanced mathematics and computer science. Any attempt to modify data breaks these cryptographic links and is quickly detected as fraudulent by the network’s computers.
What is Cryptocurrency Mining?
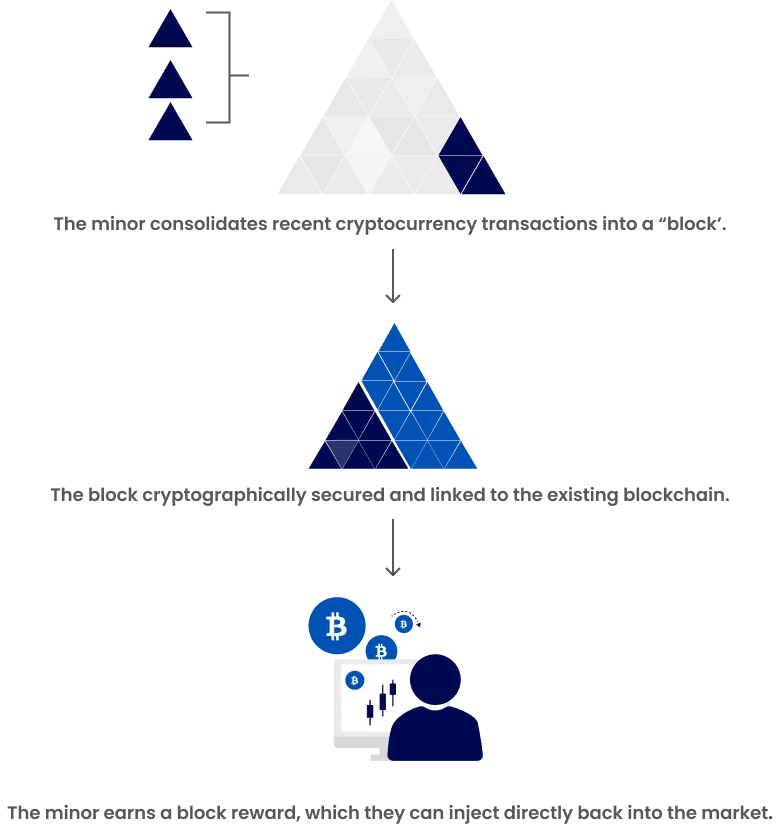
Cryptocurrency mining validates recent transactions and adds new blocks to the blockchain.
How Transactions are Verified on the Blockchain
Transaction Verification: Mining nodes select pending transactions from a pool and verify that the sender has sufficient balance to complete the transaction by cross-referencing the blockchain’s transaction history. A secondary verification confirms the sender’s authorization via their private key.
Block Creation: Mining nodes aggregate valid transactions into a new block and attempt to generate a cryptographic link to the preceding block by solving a complex computational puzzle. Upon success, the block is appended to their local blockchain copy and the update is broadcast across the network.
Figure 3: Cryptocurrency Mining Illustration
What Drives Cryptocurrency Markets?
Cryptocurrency markets are driven by supply and demand dynamics. Due to their decentralized nature, they are less influenced by many economic and political factors affecting traditional fiat currencies.
Key Factors Influencing Crypto Prices
Although uncertainty remains high, the following factors significantly impact cryptocurrency valuations:
Supply: The total circulating coins and the rate of issuance, destruction, or loss
Market Capitalization: The aggregate value of all coins in circulation and market sentiment regarding its growth
Media Coverage: The portrayal and volume of media attention a cryptocurrency receives
Integration: The degree to which a cryptocurrency is integrated into existing infrastructures, such as e-commerce payment systems
Key Events: Significant occurrences including regulatory changes, security incidents, and economic disruptions
How Crypto Trading Works with TMGM
With TMGM, you can trade cryptocurrencies via a CFD account – derivative contracts that allow you to speculate on whether the price of your selected cryptocurrency will rise or fall. Prices are quoted in fiat currencies such as the US dollar, and you do not take ownership of the underlying cryptocurrency.
CFDs are leveraged instruments, meaning you can open positions by depositing only a fraction of the trade'’s total value. While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases potential losses if the market moves against your position.
Key Terms in Crypto Trading
Understanding Crypto CFD Spreads
The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices quoted for a cryptocurrency. As with many financial markets, when opening a position on a cryptocurrency market, you' will see two prices:
To open a long position, you transact at the ask (buy) price, which is slightly above the market price
To open a short position, you transact at the bid (sell) price, which is slightly below the market price
What are Lots in Crypto Trading?
Cryptocurrencies are commonly traded in lots – standardized batches of cryptocurrency tokens to facilitate consistent trade sizes. Due to the high volatility of cryptocurrencies, lot sizes are typically small, often consisting of a single unit of the base cryptocurrency. However, some cryptocurrencies may be traded in larger lot sizes.
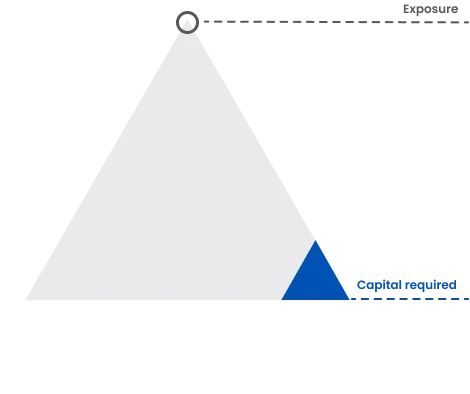
How Leverage Works in Crypto Trading
Leverage allows traders to gain exposure to larger cryptocurrency positions without paying the full trade value upfront. Instead, a margin deposit is required. Upon closing a leveraged position, profits or losses are calculated based on the full trade size.
While leverage can enhance profits, it also increases the risk of amplified losses—, including losses exceeding your initial margin on a single trade. Therefore, effective risk management in leveraged trading is critical.
Figure 3: Leverage Illustration
Crypto Margin Explained
Margin is the initial deposit required to open and maintain a leveraged position. When trading cryptocurrencies on margin, the margin requirement varies depending on your broker and the size of your trade.
Margin is typically expressed as a percentage of the total position size. For example, a Bitcoin (BTC) trade might require a 10% margin. Instead of depositing $5,000, you would only need to deposit $500.
Measuring Crypto Price Movement with Pips
Pips represent the smallest standardized unit of price movement in a cryptocurrency. For major cryptocurrencies traded at the 'dollar' level, a price change from $190.00 to $191.00 represents a one-pip move. Some lower-value cryptocurrencies may have pips measured in cents or fractions thereof.
Before trading, it is essential to review TMGM'’s platform details to understand the pip measurement scale for each cryptocurrency.
Getting Started with TMGM'’s Crypto CFD Trading
Open an Account: Register with TMGM and complete account verification
Deposit Funds: Fund your trading account using secure payment options
Choose a Cryptocurrency: Select from the available crypto CFDs
Analyze the Market: Utilize TMGM'’s analytical tools to identify trading opportunities
Set Your Position Size: Determine appropriate leverage and margin requirements
Implement Risk Management: Establish stop-loss and take-profit orders
Execute Your Trade: Enter long or short positions based on your market analysis
Monitor and Close: Track your open positions and close them when appropriate
Risk Management for Crypto Trading
Due to the high volatility of cryptocurrency markets, risk management is vital:
Use stop-loss orders to limit potential downside
Consider guaranteed stop-loss orders for added protection during volatile market events
Maintain reasonable leverage levels to avoid excessive exposure
Diversify your portfolio across various cryptocurrencies and asset classes
Never risk more than you can afford to lose
Stay updated on market news and developments
Free Crypto Trading Courses and Learning Tools
Becoming a proficient trader requires skill, knowledge, and practice. TMGM provides comprehensive free trading courses and webinars. Additionally, it offers a free demo account with US$100,000 in virtual funds, allowing you to practice risk-free and build confidence.
We also provide trading strategy insights, market analysis, and news articles tailored to all experience levels—, ensuring that whether you’ are a beginner or an experienced trader, TMGM has resources to support your trading journey.