TradingPlatformAcademyNews & AnalysisAboutPartners
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, means buying one currency and selling another at the same time, hoping to profit from changes in their exchange rates. All forex trades happen in pairs, such as EUR/USD. The forex market is the world’s largest and most liquid, open 24 hours a day, five days a week, across major financial hubs such as London, New York, and Tokyo and with daily trading volume over $6.6 trillion. Unlike stocks, forex lets you trade on both rising and falling prices, making it possible to profit in any market direction.
In this guide, you’ll discover the fundamentals of forex trading, how the forex market operates, strategies, and the benefits of trading with TMGM, a globally recognized forex broker.
Forex trading operates similarly to any financial transaction where one asset is exchanged for another. In this case, forex traders buy one currency while simultaneously selling another. The market price of a currency pair reflects how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
For example, if the GBP/USD pair is priced at 1.2500, it means 1 British pound is equivalent to 1.25 US dollars.
Each currency is identified by a three-letter code, simplifying trade execution. Below are some common currency codes:
These codes help traders quickly recognize and trade currency pairs efficiently.
Figure 1 : Illustrates different unique currency codes
All forex trading involves buying one currency while selling another, so currencies are quoted in pairs. Each forex pair represents the exchange rate between two currencies.
Major pairs always include the US dollar (USD) paired with one of seven other major currencies:
Major pairs account for approximately 75% of all forex trading volume, with EUR/USD being the most actively traded pair globally.
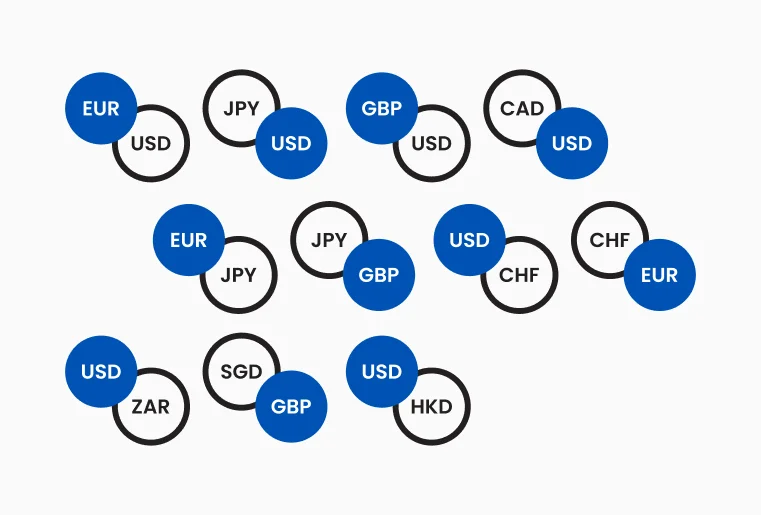
Figure 2: Illustrates major currency pairs
Every currency pair quote includes two prices:
The difference between these prices is known as the spread, and it represents one of the primary transaction costs in forex trading.

Figure 3: Illustrates Base and Quote Currencies
In the currency pair EUR/USD:
The exchange rate indicates how much-quoted currency (USD) is needed to purchase one unit of base currency (EUR). For example, if EUR/USD is quoted at 1.2000, 1 euro can be exchanged for 1.20 US dollars.

Figure 4: Illustrates One Pip
A forex pip (percentage in point) is the smallest standardized price movement in forex trading:
For example, if EUR/USD moves from 1.2000 to 1.2001, it has moved one pip. Pipettes (or fractional pips) represent a 1/10 of a pip and are shown as the fifth decimal place in most currency pairs.

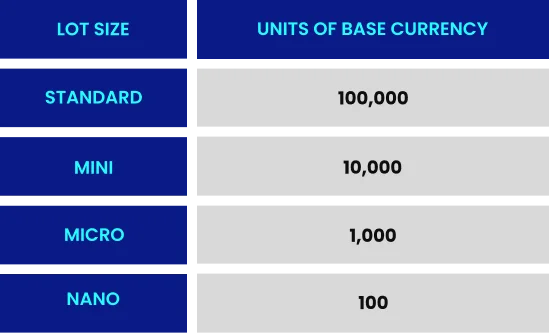
Figure 5: Illustrates One Lot
In forex trading, a "lot" refers to the standardized unit of measurement for trade size, with one standard lot equal to 100,000 units of the base currency. The size of the lot directly impacts the value of a pip. For a standard lot of EUR/USD, each pip movement represents a $10 change in value.
To calculate potential profit or loss in forex trading:For a long position (buying): Profit/Loss = (Closing Price - Opening Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
For a short position (selling): Profit/Loss = (Opening Price - Closing Price) × Lot Size × Number of Lots
Trading scenario:
Currency pair: EUR/USD
Opening position: Buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units) at 1.2000
Closing position: Sell at 1.2050
Calculation: (1.2050 - 1.2000) × 100,000 = $500 profit
Leverage allows forex traders to control a large position with a relatively small capital. It is expressed as a ratio, such as 30:1, which means you can maintain a position 30 times larger than your invested capital.
Leverage is a double-edged sword:
Margin in forex is the deposit required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It acts as collateral for the leveraged portion of the trading exposure.
For a EUR/USD trade with:
You need at least $4,000 in your account to open this position.
Leverage in trading can amplify potential gains and losses, making risk management a crucial component of a sustainable strategy.
Effective leverage management ensures controlled risk exposure and long-term sustainability in trading.
Forex trading is decentralized and operates over the counter (OTC). Instead of a central exchange, transactions occur electronically between banks, brokers, institutions, and retail traders.

Figure 6: Illustrates the forex transactions each day
The modern forex market has undergone significant transformation since its origins:
Pre-1970s: Fixed exchange rates under the Bretton Woods Agreement
1971: Transition to floating exchange rates following the collapse of Bretton Woods
1980s-1990s: Introduction of electronic trading platforms and expanded institutional access
Early 2000s: Proliferation of online retail forex brokers, democratizing access for individual traders
Present day: Advanced algorithmic trading, mobile platforms, and integration with other asset classes
Today's forex market represents a sophisticated ecosystem where central banks, commercial banks, investment firms, corporations, and retail traders interact continuously across global markets.
Central banks are crucial in shaping monetary policy, directly influencing currency values. Interest rates are a primary tool—higher rates generally strengthen a currency by attracting foreign investment seeking better returns. Quantitative easing (QE) expands the money supply, potentially weakening a currency, while quantitative tightening (QT) reduces liquidity, often leading to currency appreciation. Additionally, forward guidance, or central bank communication about future policy decisions, can significantly impact market expectations and exchange rate movements.
Major central banks that influence global currency markets include the Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of Japan (BOJ), Bank of England (BOE), and Swiss National Bank (SNB). Traders closely monitor their decisions and statements to anticipate shifts in market trends.
Key economic releases that influence forex markets: 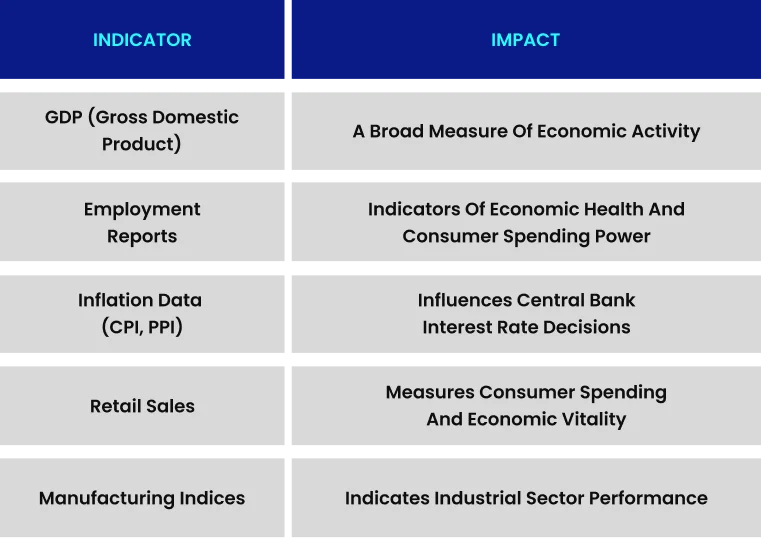
Market sentiment reflects traders' overall attitude, influencing price movements beyond fundamental data. It plays a crucial role in short-term trends and momentum-driven markets.
Understanding market sentiment allows traders to align their strategies with prevailing biases and anticipate potential shifts in market direction.
TMGM is a leading forex broker offering exceptional trading conditions, advanced technology, and comprehensive support for traders of all levels.
TMGM is a leading forex broker offering exceptional trading conditions, advanced technology, and comprehensive support for traders of all levels.
TMGM offers tight spreads starting from 0.0 pips on major currency pairs with competitive commission rates. Traders can access leverage up to 1:1000, benefiting from deep liquidity sourced from multiple tier-1 providers for efficient trade execution. The platform provides fast execution speeds, averaging under 30 milliseconds, minimizing slippage, and improving trading efficiency.
TMGM supports MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), available on pc, mac, tablet and mobile devices, catering to various trading preferences. The broker provides educational resources, including a Trading Academy, live webinars, daily market analysis, trading guides and a real-time economic calendar to keep traders informed. Clients also receive multilingual support, dedicated account managers, and efficient withdrawal processing, ensuring a seamless trading experience.
Becoming a successful Forex trader takes skill, knowledge, and practice. TMGM offers everything you need to get there, with a wealth of free forex trading courses and webinars. It also offers a free demo account with US$100,000 in virtual funds to help build your confidence in a risk-free environment.
We also provide trading strategy insights, market analysis, and news articles for all experience levels-so whether you're a complete newcomer or a seasoned trader, TMGM has something for you. Sign up for an account today!