What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading is the buying of one currency and the simultaneous selling of another in order to benefit from changes in exchange rates.
Also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, it takes place in the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily turnover of more than 6.6 trillion US dollars. For beginners, understanding how to start forex trading in India is often the first practical step.
Trading sessions run twenty four hours a day, five days a week across major financial centres such as London, New York and Tokyo, and traders need to be aware of specific forex market timings in India when planning their sessions.
All forex trading happens in currency pairs. When you buy one currency in the pair, you sell the other at the same time. Unlike many stock markets, forex trading allows traders to look for opportunities in both rising and falling markets, because you can take long positions and short positions on currency pairs.
How Does Forex Trading Work for Beginners in India?
Forex trading works by quoting currencies in pairs and letting traders speculate on whether one currency will strengthen or weaken against the other. When people ask what is forex trading and how does it work, the short answer and basic forex trading meaning is that you decide whether you expect the base currency in a pair to rise or fall in value relative to the quote currency, then place a buy or sell order accordingly.
Take the GBP USD pair as an example. If GBP USD is priced at 1.2500, it means one British pound is worth one point two five US dollars. If you believe the pound will strengthen against the dollar, you might buy the pair. If you think the pound will weaken, you might sell the pair. This direct pricing structure makes it easier for Indian traders to understand how forex trading works in real examples.
Each currency is identified by a three letter code that is used globally, including in forex trading in India. Some of the most common codes are:
USD for the US Dollar
EUR for the Euro
GBP for the British Pound
JPY for the Japanese Yen
AUD for the Australian Dollar
These codes help traders scan quotes quickly and place orders accurately in trading platforms. They also appear constantly when you learn how to read trading charts for Indian traders.

Figure 1 : Illustrates common currency codes
What are Currency Pairs, Pips and Lots in Forex Trading?
Currency pairs show the exchange rate between two currencies, while pips and lots measure price movement and trade size in forex trading. Together they form the basic language of the forex market that every beginner in India needs to understand.
How are Major, Minor and Exotic Currency Pairs Defined?
Major pairs always include the US dollar together with one of the main global currencies such as the euro, the British pound or the Japanese yen. These major currency pairs are the most actively traded in forex trading and tend to offer high liquidity and relatively tight spreads. Pairs such as EUR USD or GBP USD are examples of major pairs.
Minor pairs combine two major currencies without the US dollar, for example EUR GBP or GBP JPY. Exotic pairs combine a major currency with the currency of an emerging or smaller economy, such as USD TRY or EUR ZAR. Indian traders may follow major global pairs on international platforms while also being aware of how the Indian rupee trades on local markets that follow domestic regulations. Those markets are influenced by factors such as India’s foreign exchange reserves.
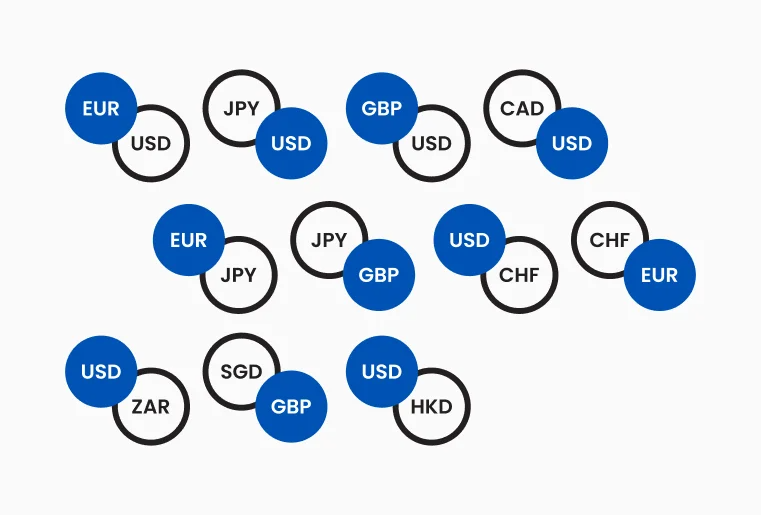
Figure 2: Illustrates major currency pair
How are Forex Pairs Quoted?
Every forex trading quote contains two prices, known as the bid and the ask. The bid is the price at which you can sell the base currency, and the ask is the price at which you can buy the base currency. The difference between the bid and the ask is called the spread, and for anyone learning how forex trading works this spread is one of the main transaction costs to be aware of when opening and closing trades.
In a typical EUR USD quote, the first currency in the pair is called the base currency and the second is called the quote currency. If EUR USD is quoted at 1.2000, it means one euro equals one point two zero US dollars. When the quote moves higher or lower, it reflects changes in the relative strength of the two currencies.

Figure 3: Illustrates Base and Quote Currencies
What is a Pip in Forex Trading?
A pip, short for percentage in point, is the smallest standardized movement in price for most forex trading pairs. For most currency pairs, a change at the fourth decimal place, such as a move from 1.2000 to 1.2001, equals one pip. For pairs that include the Japanese yen, a change at the second decimal place is usually one pip.
Some brokers also quote prices using fractional pips, known as pipettes, which are shown at the fifth decimal place and equal one tenth of a pip. Tracking pip movements helps Indian traders measure price changes, calculate potential profit or loss and compare volatility between currency pairs.

Figure 4: Illustrates One Pip
What is a Lot in Forex Trading ?
Lot size in forex trading is the standardized unit that defines the size of a position. One standard lot is equal to one hundred thousand units of the base currency in a pair, while a nano lot is only one hundred units. Between these two there are mini and micro lot sizes that give traders flexibility when choosing how much to trade.
The bigger the lot size, the greater the impact of each pip movement on your profit or loss. A one pip move in a standard lot has a much larger cash impact than the same move in a micro or nano lot. For beginners in India, understanding lot sizes is essential for controlling risk and choosing position sizes that suit the size of your trading account.

Figure 5: Illustrates One Lot
How Do You Calculate Profit and Loss in Forex Trading?
You calculate profit and loss in forex trading by multiplying the change in price by the lot size and by the number of lots you trade. For a long position, where you buy first and sell later, profit equals the closing price minus the opening price, multiplied by the lot size and the number of lots. For a short position, where you sell first and buy back later, the formula is reversed.
For example, imagine you buy one standard lot of EUR USD at 1.2000 and later close the trade by selling at 1.2050. The price has moved fifty pips in your favour. The profit is the difference between the two prices multiplied by the one hundred thousand unit lot size, which is five hundred US dollars. By learning how pips, lots and profit or loss are calculated, traders in India can make more informed decisions about trade size and risk per position.
What is Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading?
Leverage in Forex Trading
Leverage in forex trading in India allows you to control a much larger position with a relatively small amount of capital, while margin is the deposit required to open and maintain that leveraged position. Leverage is usually expressed as a ratio, such as thirty to one, which means that for every one dollar of your own money you can control thirty dollars in the market.
Leverage can amplify results in both directions. A favourable price move can lead to larger profits than you would achieve without leverage, but an unfavourable move can also lead to larger losses. That is why beginners in India need to understand how leverage works before they start trading live accounts.
Margin in Forex Trading
Margin in forex trading is the portion of your account balance that is set aside as collateral for an open position. Brokers calculate the margin required based on the value of the position and the leverage level you choose.
Initial Margin
Initial margin is the amount needed to open a position. For example, with thirty to one leverage, the initial margin is about three point three three percent of the full position value.
Maintenance Margin
Maintenance margin is the minimum equity that must remain in your account to keep the position open. If your account equity falls below this level, you may receive a margin call or have positions closed automatically.
To see how this works in practice, imagine a position in EUR USD where you buy one standard lot of one hundred thousand euros at an exchange rate of 1.2000.
The notional value of the position is one hundred twenty thousand US dollars. If the leverage is thirty to one, the initial margin required is one hundred twenty thousand divided by thirty, which is four thousand US dollars.
How Can Beginners Manage Leverage and Risk in Forex Trading?
Managing leverage wisely is essential for long term success in forex trading. Some risk management practices that Indian traders often consider include:
Using position sizing that risks only a small portion of account equity on each trade, for example around one to two percent.
Setting stop loss orders on every trade so that a single adverse move does not significantly damage the trading account.
Aiming for a positive risk reward ratio, where the potential profit on a trade is larger than the potential loss.
Choosing lower leverage levels than the maximum available until you gain more experience.
Stress testing strategies in periods of high volatility using historical data or demo accounts.
By choosing conservative leverage and combining it with disciplined risk management, Indian beginners can explore what forex trading means while keeping risk under better control.
Is Forex Trading Right for Beginners in India?
Forex trading in India offers beginners a way to participate in the world currency market, which is one of the largest and most liquid financial markets in existence. Before you begin, it is important to clarify is forex trading legal in India so you understand the regulatory framework you are operating in. You may also want to review how forex trading is taxed in India so that potential profits and losses fit within your broader financial planning. By understanding what forex trading is, how it works and what it means in the Indian context, you can better judge whether it aligns with your financial goals, time commitment and tolerance for risk.
If you decide to explore forex trading, it is wise to start with education and a demo account, then move to live trading gradually with a well defined plan. Some traders also take time to reflect on whether forex trading is halal or haram in India based on their personal beliefs. When you are ready to choose a provider, you can compare what matters to you in a CFD broker for traders in India. This can help you narrow down options and focus on what you consider the best forex broker in India for your needs. Working with a reputable broker such as TMGM, and always staying informed about the latest regulations that apply to forex trading in India, can help you take your next steps more confidently.