Key Takeaways
- While day trading focuses on capturing intraday price movements and avoiding overnight exposure, sustained success relies on disciplined strategy development and rigorous risk management rather than solely on trading tools.
- Effective Day Trading Strategies include trend-following methods (using Moving Averages and MACD), reversal patterns (such as RSI signals and double tops/bottoms), and breakout techniques (range breakouts and opening-range breakouts), each with clearly defined entry points, stop-loss levels, and profit targets.
- Always seek Confluence for Confirmation —Moving Averages, RSI/Stochastics, Bollinger Bands, VWAP, ATR—combined with high-probability chart patterns and volume validation to time entries and set adaptive stop-losses.
- Consistency in profitable day trading improves when traders effectively manage emotions like fear, greed, and revenge trading through probabilistic thinking, process adherence, strict rule compliance, and ongoing journaling and performance review.
- A robust trading system documents market conditions, setups, entry and exit rules, and position sizing guidelines, then verifies its edge through backtesting and live simulated trading before deploying real capital.
- Risk management is fundamental: limit risk to 1–2% per trade using the formula Position Size = Money at Risk ÷ Stop-Loss, apply fixed, ATR-based, or technical stops, cap drawdowns, and target a risk-reward ratio of at least ≥1:2.
Day Trading Strategy Fundamentals for Beginners
Understanding Market Structure in Day Trading
This guide covers profitable CFD trading strategies, technical analysis techniques, and risk management practices employed by experienced traders. It assists both beginners and advanced traders in refining their approach for consistent profitability. Before applying any CFD day trading strategy, it's crucial to understand the structure of the market you're trading. Different markets—stocks, forex, futures, or cryptocurrencies—each exhibit unique characteristics:
Stock Markets: Influenced by company fundamentals, sector trends, and overall market sentiment
Forex Markets: Driven by macroeconomic indicators, interest rate differentials, and geopolitical developments
Futures Markets: Affected by supply and demand dynamics, seasonality, and underlying spot markets
Cryptocurrency Markets: Impacted by technological advancements, regulatory updates, and adoption rates
Understanding these structural differences helps determine which strategies are most effective under specific market conditions.
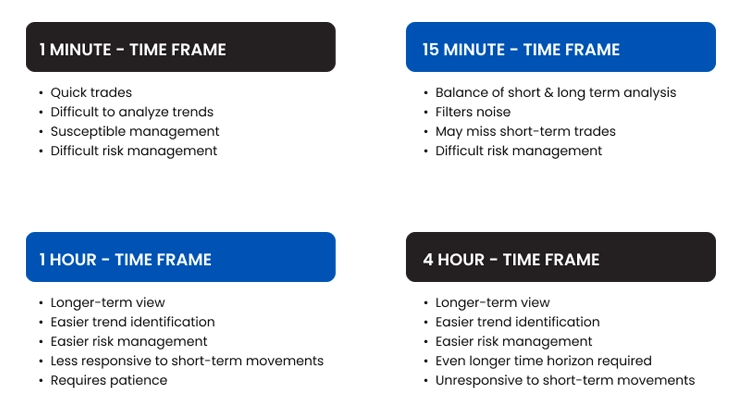
Selecting the Right Time Frames for Your Day Trading Strategy
Day traders usually focus on shorter time frames, but successful traders often use multi-timeframe analysis:
1-minute and 5-minute charts: Used for precise entry and exit timing
15-minute and 30-minute charts: Assist in identifying intraday trends and support/resistance zones
1-hour and 4-hour charts: Provide context for broader intraday trends
Daily charts: Offer perspective on key levels and overall market direction
Employing multiple time frames delivers a comprehensive market view and helps filter out false signals common in lower time frames.
Figure 1: Informational chart titled "Day Trading Time Frames", illustrating various time frames used in day trading along with their benefits and limitations
Core Risk-Management Principles for Traders
Before delving into specific strategies, it's essential to establish sound risk management principles. A fundamental rule is to never risk more than 1-2% of your trading capital on any single trade, keeping losses manageable. Maintaining a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:1.5, ideally 1:2 or higher, helps optimize gains relative to potential losses.
Hard stop-loss orders are crucial to protect against unexpected market moves and limit drawdowns. Additionally, tracking performance metrics enables traders to identify strengths and weaknesses for ongoing improvement. These fundamentals underpin profitable and sustainable day trading strategies.
Top Profitable Day Trading Strategies
Trend-Following Strategy That Works
Trend following remains one of the most dependable day trading approaches, based on the premise that prices tend to continue moving in the current direction until a significant reversal occurs.
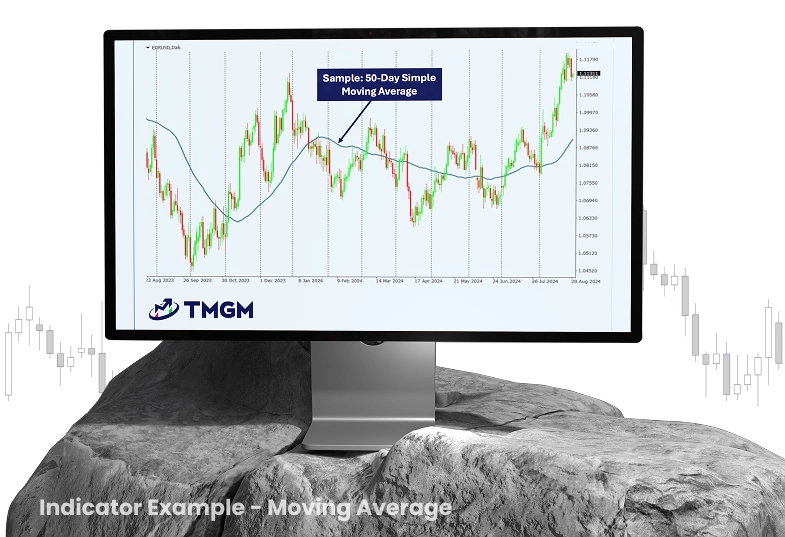
Mastering the Moving-Average Trading Strategy
Figure 2: Technical analysis chart displaying the EUR/USD currency pair on a daily timeframe with a 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) applied
This strategy employs moving averages to determine trend direction and potential entry signals:
Plot two moving averages—commonly a 20-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and a 50-period EMA
Enter long positions when the shorter MA crosses above the longer MA
Enter short positions when the shorter MA crosses below the longer MA
Place stop-loss orders below recent swing lows (for long trades) or above recent swing highs (for short trades)
Take profits at predefined levels or when moving averages indicate a potential trend reversal
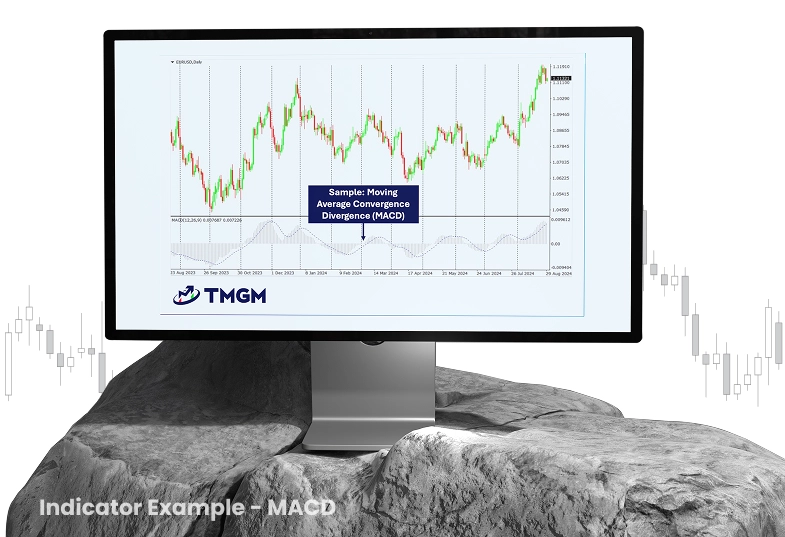
MACD Trend-Trading: Day Trading Tool
Figure 3: Technical chart demonstrating the use of the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator on the EUR/USD daily chart
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator assists in identifying trend momentum and potential reversals:
Enter long positions when the MACD line crosses above the signal line during an uptrend
Enter short positions when the MACD line crosses below the signal line during a downtrend
Confirm signals with supplementary indicators such as RSI or volume
Exit positions when the MACD line crosses back in the opposite direction
Reversal-Trading Strategy to Capture Market Turns
Reversal strategies aim to capture early stages of new trends as market direction changes.
Oversold/Overbought Reversals
Figure 4: Technical chart illustrating overbought and oversold conditions, typically identified using momentum oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Stochastic Oscillator.
This strategy utilizes momentum oscillators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to pinpoint potential reversal zones:
Identify extreme overbought conditions (RSI above 70) or oversold conditions (RSI below 30)
Look for divergence between price and oscillator (price makes new highs/lows while the indicator does not)'
Wait for confirmation candlestick patterns (engulfing, hammer, shooting star, etc.)
Enter positions with tight stop-losses placed beyond the extreme price points
Take profits at key support/resistance levels or when momentum diminishes
Double-Top & and Double-Bottom Formations Explained
This pattern-based strategy targets reversals at significant technical levels:
Identify markets that have tested the same support or resistance level twice
Enter short positions when price breaks below the "neckline" following a double top
Enter long positions when price breaks above the "neckline" following a double bottom
Place stop-loss orders just above/below the pattern
Target profit levels equal to the height of the pattern
Breakout Trading Strategies: Ideal for High Alpha Returns
Figure 5: Depicts a resistance breakout, a fundamental concept in technical analysis used to identify potential trend continuations or reversals
Breakout strategies exploit significant price moves when markets breach established support or resistance levels.
Range-Breakout Strategy: Capturing Early Momentum
Identify markets trading within a defined range bounded by clear support and resistance
Monitor for price approaching range boundaries accompanied by rising volume
Enter long positions on a breakout above resistance or short positions on a breakdown below support
Place stop-loss orders just inside the broken range
Set profit targets equal to the range height
Opening-Range Breakout for Intraday Gains
This strategy leverages the initial trading range established during market open:
Define the high and low of the first 30 minutes (or first hour) of trading
Enter long positions when price breaks above the opening range high
Enter short positions when price breaks below the opening range low
Place stop-loss orders at the opposite end of the range
Take profits at key support/resistance levels or employ trailing stops
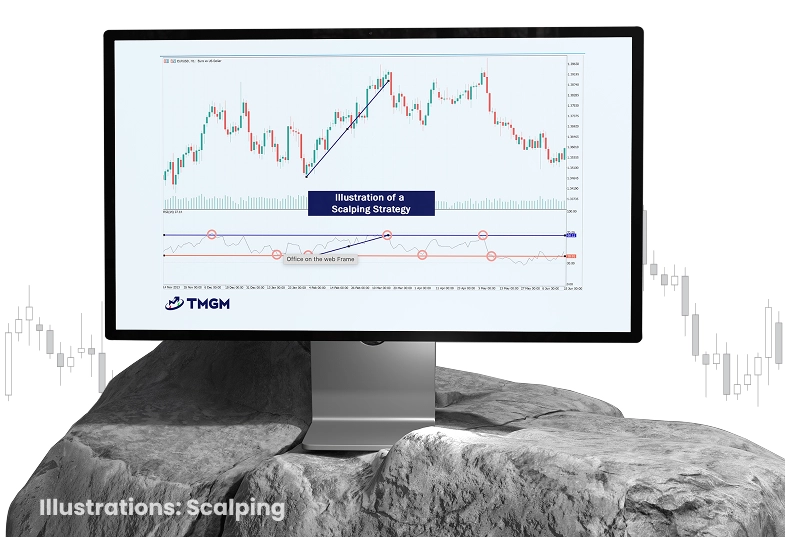
Scalping Techniques: Rapid Profit Opportunities
Figure 6: Demonstrates a scalping strategy applied to a EUR/USD forex chart on an H1 (hourly) timeframe
Scalping involves executing numerous trades daily to capitalize on small price fluctuations.
Bid-Ask Spread Scalping Techniques
This method is especially effective in forex and futures markets:
Select assets with tight bid-ask spreads
Trade in the direction of the immediate short-term trend
Target profits of 5-10 pips or ticks
Use tight stop-losses, typically 2-5 pips or ticks
Exit positions rapidly, often within minutes
Order-Flow Scalping: Analyzing Market Depth
This advanced technique leverages order flow data to detect institutional buying and selling activity:
Utilize time and sales data and/or depth of market (DOM) information
Identify large orders or imbalances between buy and sell orders
Trade in the direction of dominant order flow
Exit when order flow imbalances diminish
Maintain strict risk management with predefined stop-loss levels
Gap-Trading Techniques for Intraday Moves
Gap trading exploits price gaps occurring between the previous market close and the next day's open.
Gap-Fill Strategy: Trading Overnight Gaps
Identify stocks or futures opening with a significant gap relative to the prior day's close.
Analyze the gap type (common, breakaway, runaway, or exhaustion gap)
For common gaps, enter trades anticipating the gap will fill (price returns to previous close)
For breakaway or runaway gaps, trade in the direction of the gap
Place stop-loss orders beyond key support/resistance levels
Take profits when the gap fills or at predetermined targets
Essential Technical Analysis Tools for Day Trading Strategies
Key Technical Indicators
Successful day traders typically combine the following technical indicators:
Moving Averages (SMA and EMA): Identify trend direction and key support/resistance levels
Using RSI for Overbought/Oversold Conditions: Measure overbought and oversold market states
Stochastic Oscillator for Timing Entries: Identify potential reversal points
Bollinger Bands for Volatility Breakouts: Assess volatility and potential price targets
VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price) Techniques: Intraday benchmark for price action
ATR-Based Stop-Loss Placement: Use Average True Range (ATR) to adjust stop-loss distances based on market volatility
The key is to avoid overloading with indicators; instead, select complementary tools that address different facets of price behavior.
Chart Patterns Every Day Trader Should Master
Recognizing high-probability chart patterns significantly enhances trading outcomes by providing insights into potential price trajectories. Continuation patterns like flags, pennants, and triangles suggest trend persistence. Reversal patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and island reversals indicate possible trend changes and critical market turning points.
Additionally, candlestick patterns including engulfing, doji, hammer, and shooting star offer valuable clues about market sentiment and momentum shifts. Each pattern aids traders in identifying optimal entry and exit points, as well as natural stop-loss and take-profit placements, improving risk control and strategy execution.
Volume-Analysis Techniques for Enhanced Entries
Volume confirms price action and provides critical insights:
Spotting Volume Spikes for Confirmation: Often signal potential reversals or breakouts
Identifying Volume Divergence to Validate Trends: Occurs when price makes new highs/lows without volume confirmation'
Leveraging Relative Volume Effectively: Comparing current volume against average volume highlights unusual activity
Day traders should always corroborate price signals with volume data to increase trade probability.
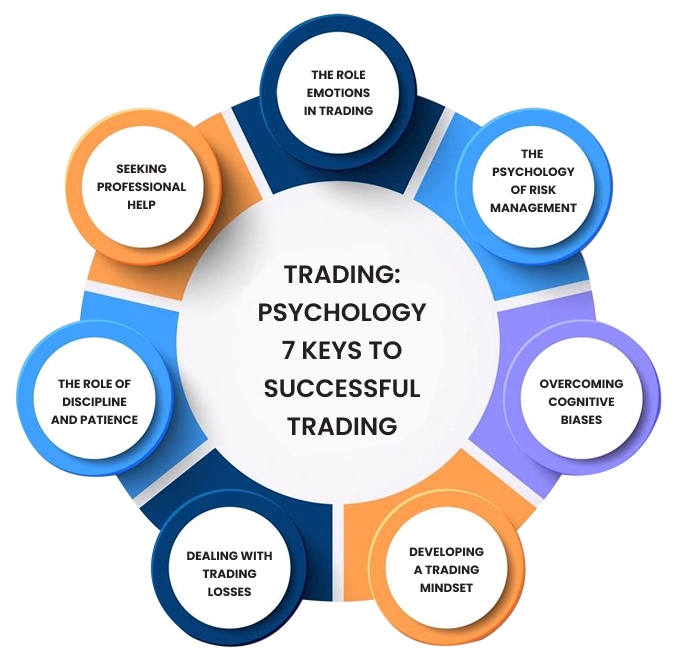
Psychological Aspects of Successful Day Trading Strategies
Managing Emotions During Live Trading
Emotional regulation is a critical differentiator between profitable and unprofitable day traders. Fear can cause premature exits or hesitation to enter valid setups. Greed may lead to overholding positions or increasing size imprudently. Revenge trading—the attempt to recoup losses through high-risk trades—is particularly harmful. Successful traders develop systematic methods to manage these emotions and maintain discipline.
Cultivating a Winning Trading Mindset
A proper mindset is essential for long-term success. Probability thinking helps traders accept that no trade is guaranteed. Process orientation shifts focus from immediate P&L to strategy execution. Emotional detachment enables unbiased decision-making. Continuous learning ensures each trade contributes to improvement.
Building Discipline for Consistent Results
Discipline entails strict adherence to a trading plan and risk management rules without exceptions. Traders should only take setups that meet predefined criteria. Maintaining detailed trading journals facilitates performance tracking and identifies improvement areas. Regular trade reviews keep traders aligned and enable strategy refinement.
Figure 7: Outlines seven key psychological principles successful traders should master.
Building Your Day Trading Strategy System
A comprehensive trading plan is vital for consistency and structure in day trading. It should specify markets and time frames, detailed entry and exit criteria, position sizing rules, and risk management protocols. Establishing a trading schedule promotes discipline, and a performance review process facilitates continuous strategy enhancement. The plan should be documented clearly enough for another trader to execute it precisely.
How to Backtest Your Day-Trading Strategy
Before risking real capital, traders must backtest strategies to assess performance and reliability. This involves applying strategy rules to historical price data for the target markets.
Recording hypothetical trades and outcomes provides insights into profitability, while key metrics like win rate, profit factor, and drawdown measure risk and consistency. Traders can refine strategies based on these results before live deployment.
Forward-Testing & Paper-Trading Best Practices
After backtesting, traders should conduct real-time paper trading to evaluate execution quality, emotional responses, and practical challenges not evident in backtesting.
Final adjustments can be made before transitioning to live trading, starting with small position sizes to manage risk and build confidence.
Risk Management in Day Trading Strategies
Risk management is the cornerstone of successful day trading. Even the best setups can incur losses without proper controls. Here’s how to manage risk effectively:
Position-Sizing Fundamentals
Position sizing determines the capital exposure per trade.
Risk per trade: Limit to 1-2% of total account equity per trade.
Position-Size Formula: Position Size = Money at Risk ÷ Stop-Loss in Pips (or Points)
Managing Drawdowns to Sustain Trading: For example, with a $20,000 account risking 1% per trade ($200) and a stop-loss of 20 pips, position size equals $200 ÷ 20 pips = $10 per pip.
Leverage Caution - Use Margin Responsibly: Higher leverage increases risk exposure. Always align leverage with your risk tolerance.
Setting Stop-Losses to Protect Capital
A stop-loss order limits losses if the market moves against your position.
Types of stop-losses:
Fixed stop-loss: A predetermined percentage (e.g., 1% of capital).
ATR-based stop-loss: Uses the Average True Range (ATR) to adjust stop distance according to volatility.
Technical stop-loss: Placed at support/resistance levels, trendlines, or moving averages.
Trailing stop-loss: Moves in your favor to lock in profits while limiting downside risk.
Example:
Buy at $100 with a 2% stop-loss → set at $98.
In forex, if ATR is 15 pips, the stop-loss could be 1.5 × ATR = 22.5 pips.
Managing Drawdowns to Sustain Trading
A drawdown is the decline in account equity following a series of losses.
Max drawdown limit: Cease trading if monthly drawdown reaches 5-10%.
Risk-reward ratio: Target at least 1:2 risk-reward (risk $1 to make $2).
Reducing risk during losing streaks:
If losses persist, halve your risk per trade.
Reassess strategy——are market conditions unfavorable, or is execution flawed?
Example:
A trader with $10,000 loses $1,000 (10% drawdown).
They reduce position sizes and focus on higher-probability setups.
Elevate Your Day Trading Strategies with TMGM
Executing profitable day trading strategies requires expertise and the right trading environment. TMGM offers traders an optimal platform to implement these strategies effectively:Lightning-Fast Execution:
Minimize slippage and execute trades swiftly Execute your day trading strategies with minimal slippage
Competitive Spreads for Cost Efficiency: Maximize profitability with tight spreads across all asset classes
Advanced Trading Platforms: Access professional-grade charting, indicators, and order execution tools
Multi-Asset Trading: Apply your strategies across forex, equities, indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies
Top Risk-Management Tools for Day Traders: Utilize guaranteed stop-loss orders and other advanced risk controls
Best Educational Resources for Beginners: Enhance your trading skills with TMGM's comprehensive educational content
Leverage 24/5 Expert Support from TMGM: Receive assistance anytime from experienced trading professionals
Whether you focus on trend following, breakout, or scalping strategies, TMGM provides professional infrastructure, advanced trading tools, and our trading academy to execute your day trading plan with precision.
Ready to implement these profitable day trading strategies? Open an account with TMGM today and discover how a professional trading environment can enhance your trading performance.